Page 157 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 157
Discharge in gallons per day
100,000
100
2 2
80
60
50
5.0
40
4.0
30
20
3.0
10 10,000 20,000 Diameter 2” 40,000 2.0 1 2.5 3.5 3 4.5 200,000 6.0 4 7.0 400,000 5 6 7 1,000,000 8 9 10 2,000,000 11 12 13 14 4,000,000 15 16 10,000,000 5.2 Fluid Transport 135
8 18 20 22
6 1.5 24
5 4 3 1 1.0
Loss of head in feet per thousand 0.8 2 2 2 0.4 3 0.6 0.8 4 5 6 7 8 9
1.0
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24
0.1 Velocity in feet per second 26 28 30 33
0.08 36 39 42
0.06 48
0.2 54
0.05 60
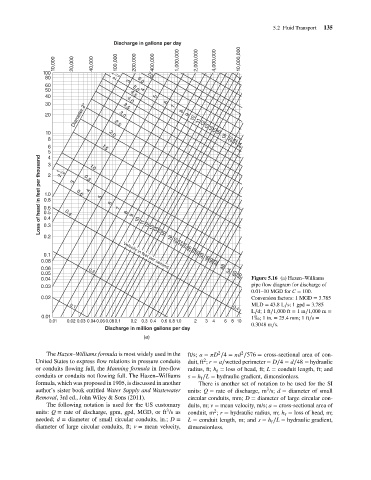
0.04 66 Figure 5.16 (a) Hazen–Williams
0.03 pipe flow diagram for discharge of
0.01–10 MGD for C = 100.
0.02 Conversion factors: 1 MGD = 3.785
MLD = 43.8L∕s; 1 gpd = 3.785
0.1
0.4
L∕d; 1 ft∕1,000 ft = 1m∕1,000 m =
0.01 1 ;1 in. = 25.4 mm; 1 ft∕s =
0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.06 0.080.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 2 3 4 6 8 10
0.3048 m∕s.
Discharge in million gallons per day
(a)
2
2
The Hazen–Williams formula is most widely used in the ft/s; a = D ∕4 = d ∕576 = cross-sectional area of con-
2
United States to express flow relations in pressure conduits duit, ft ; r = a∕wetted perimeter = D∕4 = d∕48 = hydraulic
or conduits flowing full, the Manning formula in free-flow radius, ft; h = loss of head, ft; L = conduit length, ft; and
f
conduits or conduits not flowing full. The Hazen–Williams s = h ∕L = hydraulic gradient, dimensionless.
f
formula, which was proposed in 1905, is discussed in another There is another set of notation to be used for the SI
3
author’s sister book entitled Water Supply and Wastewater units: Q = rate of discharge, m /s; d = diameter of small
Removal, 3rd ed., John Wiley & Sons (2011). circular conduits, mm; D = diameter of large circular con-
The following notation is used for the US customary duits, m; v = mean velocity, m/s; a = cross-sectional area of
3
units: Q = rate of discharge, gpm, gpd, MGD, or ft /s as conduit, m ; r = hydraulic radius, m; h = loss of head, m;
2
f
needed; d = diameter of small circular conduits, in.; D = L = conduit length, m; and s = h ∕L = hydraulic gradient,
f
diameter of large circular conduits, ft; v = mean velocity, dimensionless.