Page 160 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 160
138
Chapter 5
Water Hydraulics, Transmission, and Appurtenances
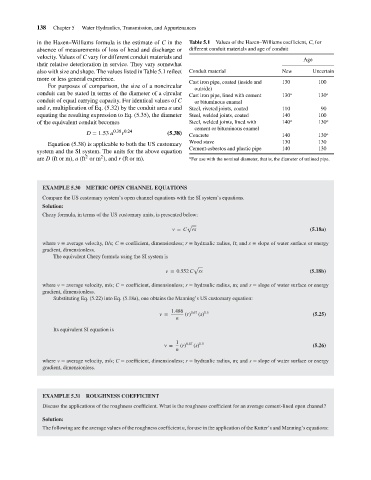
in the Hazen–Williams formula is the estimate of C in the
different conduit materials and age of conduit
absence of measurements of loss of head and discharge or
velocity. Values of C vary for different conduit materials and
Age
their relative deterioration in service. They vary somewhat
New
Uncertain
also with size and shape. The values listed in Table 5.1 reflect
Conduit material
more or less general experience.
130
100
Cast iron pipe, coated (inside and
For purposes of comparison, the size of a noncircular
outside)
conduit can be stated in terms of the diameter of a circular
a
130
Cast iron pipe, lined with cement
130
conduit of equal carrying capacity. For identical values of C
or bituminous enamel
and s, multiplication of Eq. (5.32) by the conduit area a and
Steel, riveted joints, coated
110
equating the resulting expression to Eq. (5.35), the diameter
Steel, welded joints, coated
100
140
a
140
130
Steel, welded joints, lined with
of the equivalent conduit becomes Table 5.1 Values of the Hazen–Williams coefficient, C,for 90 a a
cement or bituminous enamel
D = 1.53 a 0.38 0.24 (5.38) Concrete 140 130 a
r
Equation (5.38) is applicable to both the US customary Wood stave 130 130
Cement-asbestos and plastic pipe 140 130
system and the SI system. The units for the above equation
2
2
are D (ft or m), a (ft or m ), and r (ft or m). a For use with the nominal diameter, that is, the diameter of unlined pipe.
EXAMPLE 5.30 METRIC OPEN CHANNEL EQUATIONS
Compare the US customary system’s open channel equations with the SI system’s equations.
Solution:
Chezy formula, in terms of the US customary units, is presented below:
√
v = C rs (5.18a)
where v = average velocity, ft/s; C = coefficient, dimensionless; r = hydraulic radius, ft; and s = slope of water surface or energy
gradient, dimensionless.
The equivalent Chezy formula using the SI system is
√
v = 0.552 C rs (5.18b)
where v = average velocity, m/s; C = coefficient, dimensionless; r = hydraulic radius, m; and s = slope of water surface or energy
gradient, dimensionless.
Substituting Eq. (5.22) into Eq. (5.18a), one obtains the Manning’s US customary equation:
1.486 0.67 0.5
v = (r) (s) (5.25)
n
Its equivalent SI equation is
1 0.67 0.5
v = (r) (s) (5.26)
n
where v = average velocity, m/s; C = coefficient, dimensionless; r = hydraulic radius, m; and s = slope of water surface or energy
gradient, dimensionless.
EXAMPLE 5.31 ROUGHNESS COEFFICIENT
Discuss the applications of the roughness coefficient. What is the roughness coefficient for an average cement-lined open channel?
Solution:
The following are the average values of the roughness coefficient n, for use in the application of the Kutter’s and Manning’s equations: