Page 298 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 298
276
Chapter 9
Cross-Connection Control
resisted, will produce motion. Weight is a type of force result-
Roof-mounted solar panels
ing from gravitational attraction. Pressure (P) is a force-per-
2
2
unit area, such as lb/in. (psi) or kN/m (kPa). Atmospheric
pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of the atmo-
Heat exchanger
sphere above Earth.
Utility
Pressure may be referred to using an absolute scale,
sink
2
2
lb/in. absolute (psia) or kN/m absolute (kPa absolute). Pres-
2
sure may also be referred to using a gauge scale, lb/in. gauge
2
(psig) or kN/m gauge (kPa gauge). Absolute pressure and
gauge pressure are related. Absolute pressure is equal to the
gauge pressure plus the atmospheric pressure. At sea level
the atmospheric pressure is 14.7 psia using the US customary
units. Thus,
Sink
P = P + 14.7 psi (US customary units) (9.1)
absolute gauge
or
Sink
P gauge = P absolute − 14.7 psi (US customary units) (9.2)
In the SI units where P and P areinkPa
Coffee absolute gauge
2
2
machine (1 kPa = 1000 Pa = 1000 N/m = 1kN/m ) their relationship
can be given as follows:
P absolute = P gauge + 102 kPa (SI units) (9.3)
or
Sink
P = P − 102 kPa (SI units) (9.4)
gauge absolute
In essence then, absolute pressure is the total pressure.
Gauge pressure is simply the pressure read on a gauge. If
Chemical
Water feeder there is no pressure on the gauge other than atmospheric, the
fountatin gauge would read zero. Then the absolute pressure would
be equal to 14.7 psi (102 kPa), which is the atmospheric
Booster pump pressure.
The term vacuum indicates that the absolute pressure is
Meter less than the atmospheric pressure and that the gauge pres-
Water main sure is negative. A complete or total vacuum would mean a
Backpressure
Recommended installation backflow pressure of 0 psia or −14.7 psig (−102 kPa gauge). Because
of backflow preventers it is impossible to produce a total vacuum, the term vacuum,
as used in the text, will mean all degrees of partial vacuum.
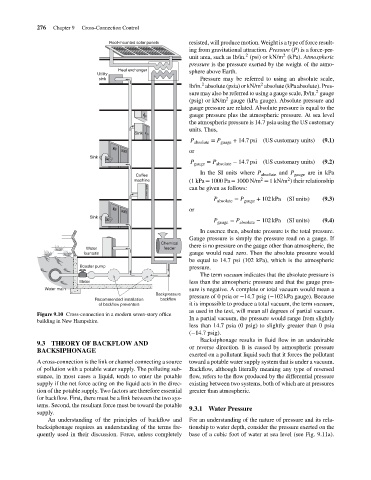
Figure 9.10 Cross-connection in a modern seven-story office
In a partial vacuum, the pressure would range from slightly
building in New Hampshire.
less than 14.7 psia (0 psig) to slightly greater than 0 psia
(−14.7 psig).
Backsiphonage results in fluid flow in an undesirable
9.3 THEORY OF BACKFLOW AND
or reverse direction. It is caused by atmospheric pressure
BACKSIPHONAGE
exerted on a pollutant liquid such that it forces the pollutant
A cross-connection is the link or channel connecting a source toward a potable water supply system that is under a vacuum.
of pollution with a potable water supply. The polluting sub- Backflow, although literally meaning any type of reversed
stance, in most cases a liquid, tends to enter the potable flow, refers to the flow produced by the differential pressure
supply if the net force acting on the liquid acts in the direc- existing between two systems, both of which are at pressures
tion of the potable supply. Two factors are therefore essential greater than atmospheric.
for backflow. First, there must be a link between the two sys-
tems. Second, the resultant force must be toward the potable
9.3.1 Water Pressure
supply.
An understanding of the principles of backflow and For an understanding of the nature of pressure and its rela-
backsiphonage requires an understanding of the terms fre- tionship to water depth, consider the pressure exerted on the
quently used in their discussion. Force, unless completely base of a cubic foot of water at sea level (see Fig. 9.11a).