Page 45 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 45
2.1 Sources of Surface Water
Intake crib,
tower, or
gatehouse
Vertical
Footbridge
pump
To
treatment plant
Inlets
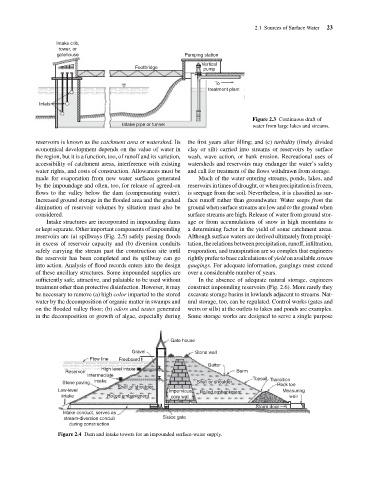
Intake pipe or tunnel Pumping station Figure 2.3 Continuous draft of 23
water from large lakes and streams.
reservoirs is known as the catchment area or watershed.Its the first years after filling; and (c) turbidity (finely divided
economical development depends on the value of water in clay or silt) carried into streams or reservoirs by surface
the region, but it is a function, too, of runoff and its variation, wash, wave action, or bank erosion. Recreational uses of
accessibility of catchment areas, interference with existing watersheds and reservoirs may endanger the water’s safety
water rights, and costs of construction. Allowances must be and call for treatment of the flows withdrawn from storage.
made for evaporation from new water surfaces generated Much of the water entering streams, ponds, lakes, and
by the impoundage and often, too, for release of agreed-on reservoirs in times of drought, or when precipitation is frozen,
flows to the valley below the dam (compensating water). is seepage from the soil. Nevertheless, it is classified as sur-
Increased ground storage in the flooded area and the gradual face runoff rather than groundwater. Water seeps from the
diminution of reservoir volumes by siltation must also be ground when surface streams are low and to the ground when
considered. surface streams are high. Release of water from ground stor-
Intake structures are incorporated in impounding dams age or from accumulations of snow in high mountains is
or kept separate. Other important components of impounding a determining factor in the yield of some catchment areas.
reservoirs are (a) spillways (Fig. 2.5) safely passing floods Although surface waters are derived ultimately from precipi-
in excess of reservoir capacity and (b) diversion conduits tation, the relations between precipitation, runoff, infiltration,
safely carrying the stream past the construction site until evaporation, and transpiration are so complex that engineers
the reservoir has been completed and its spillway can go rightly prefer to base calculations of yield on available stream
into action. Analysis of flood records enters into the design gaugings. For adequate information, gaugings must extend
of these ancillary structures. Some impounded supplies are over a considerable number of years.
sufficiently safe, attractive, and palatable to be used without In the absence of adequate natural storage, engineers
treatment other than protective disinfection. However, it may construct impounding reservoirs (Fig. 2.6). More rarely they
be necessary to remove (a) high color imparted to the stored excavate storage basins in lowlands adjacent to streams. Nat-
water by the decomposition of organic matter in swamps and ural storage, too, can be regulated. Control works (gates and
on the flooded valley floor; (b) odors and tastes generated weirs or sills) at the outlets to lakes and ponds are examples.
in the decomposition or growth of algae, especially during Some storage works are designed to serve a single purpose
Gate house
Gravel Stone wall
Flow line Freeboard
Gutter
High level intake
Reservoir Berm
Intermediate
intake Topsoil Transition
Stone paving Shell or shoulder Rock toe
Shell or shoulder
Low-level Impervious Rolled embankment Measuring
intake Rolled embankment core wall weir
Storm door
Intake conduct, serves as
stream-diversion conduit Sluice gate
during construction
Figure 2.4 Dam and intake towers for an impounded surface-water supply.