Page 127 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 127
3-24 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
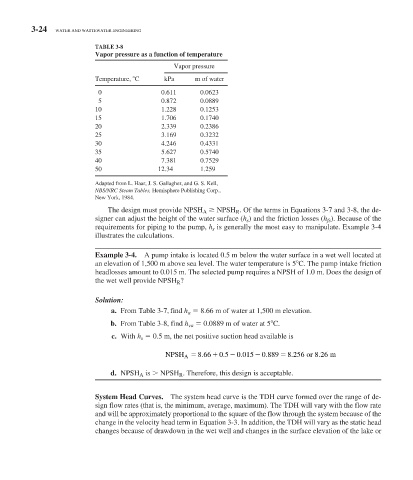
TABLE 3-8
Vapor pressure as a function of temperature
Vapor pressure
Temperature, C kPa m of water
0 0.611 0.0623
5 0.872 0.0889
10 1.228 0.1253
15 1.706 0.1740
20 2.339 0.2386
25 3.169 0.3232
30 4.246 0.4331
35 5.627 0.5740
40 7.381 0.7529
50 12.34 1.259
Adapted from L. Haar, J. S. Gallagher, and G. S. Kell,
NBS/NRC Steam Tables, Hemisphere Publishing Corp.,
New York, 1984.
The design must provide NPSH A NPSH R . Of the terms in Equations 3-7 and 3-8, the de-
signer can adjust the height of the water surface ( h s ) and the friction losses ( h fs ). Because of the
requirements for piping to the pump, h s is generally the most easy to manipulate. Example 3-4
illustrates the calculations.
Example 3-4. A pump intake is located 0.5 m below the water surface in a wet well located at
an elevation of 1,500 m above sea level. The water temperature is 5 C. The pump intake friction
headlosses amount to 0.015 m. The selected pump requires a NPSH of 1.0 m. Does the design of
the wet well provide NPSH R ?
Solution:
,
a. From Table 3-7 find h a 8.66 m of water at 1,500 m elevation.
b. From Table 3-8 , find h va 0.0889 m of water at 5 C.
c. With h s 0.5 m, the net positive suction head available is
.
.
.
.
.
.
NPSH A 866 0 5 0015 0 889 8 256 or 8 26 m
d. NPSH A is NPSH R . Therefore, this design is acceptable.
System Head Curves. The system head curve is the TDH curve formed over the range of de-
sign flow rates (that is, the minimum, average, maximum). The TDH will vary with the flow rate
and will be approximately proportional to the square of the flow through the system because of the
change in the velocity head term in Equation 3-3. In addition, the TDH will vary as the static head
changes because of drawdown in the wet well and changes in the surface elevation of the lake or