Page 92 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 92
Welding Robots
78
sensors must be applied. The most common use of sensors are (i) optical sensors
that use a laser light source on the weld joint under study and a sensor with a
narrow bandwidth filter to extract the information of interest, and (ii) through-arc
sensing that uses the electrical parameters from the arc together with knowledge
about the motion of the weld torch which is controlled by the robot.
3.2.1 Optical Sensors
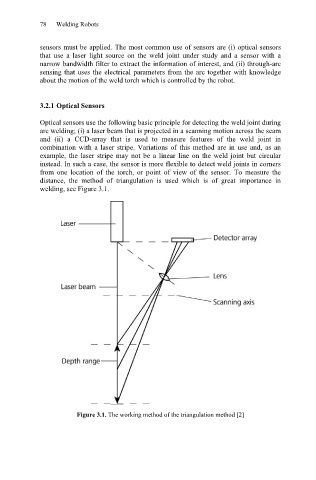
Optical sensors use the following basic principle for detecting the weld joint during
arc welding; (i) a laser beam that is projected in a scanning motion across the seam
and (ii) a CCD-array that is used to measure features of the weld joint in
combination with a laser stripe. Variations of this method are in use and, as an
example, the laser stripe may not be a linear line on the weld joint but circular
instead. In such a case, the sensor is more flexible to detect weld joints in corners
from one location of the torch, or point of view of the sensor. To measure the
distance, the method of triangulation is used which is of great importance in
welding, see Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1. The working method of the triangulation method [2]