Page 104 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 104
87
Models
interpretation
a) Updip Shooting b) Downdip Shooting X <= Apparent Velocity High Low Apparent Velocity _ ==> X - “ \ \ \ \ receivers in a downdip Seismic survey of a dipping refractor. a) Selected raypaths shooting toward 4.13 FIGURE apparent velocity (V.,) lower an emerge at a shallow angle, resulting in refraction direction. Raypaths for the critical apparent a steeper angle; an the source, rays
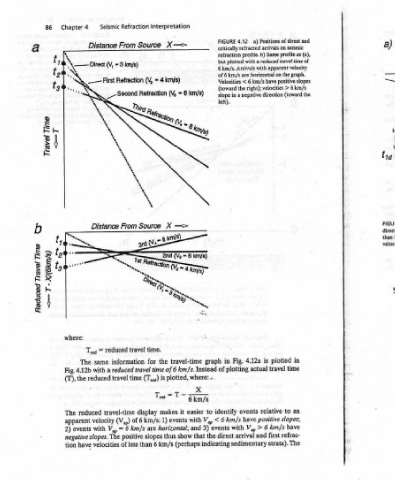
Positions of direct and arrivals on seismic Same profile as (a), reduced travel time of apparent velocity graph. the 6 km/s have positive slopes 6 km/s > the (toward in plotted time travel an to relative have positive slopes; have km/s refrac- first The strata).
a) profile. b) a are horizontal on the right); velocities negative direction is 4.12a actual 6 > V,, and sedimentary
4.12 critically refracted but plotted with 6 km/s. Arrivals with < a Fig. events with arrival
FIGURE refraction of 6 km/s Velocities (toward in slope left). in of plotting identify km/s 6 events direct
graph Instead «. =e km/s to easier < V,,, with 3) and the that indicating
Interpretation X => time. travel-time the km/s. of 6 time plotted, where: is Teg = T - 6 it makes events 1) horizontal; show thus slopes (perhaps km/s 6
Refraction Source From travel for information travel reduced (T,,4) time display km/s: of 6 (V,,) are km/s 6 positive than of less
Seismic Distance reduced = same a with travel reduced travel-time velocity = V,, with velocities
4 Teg The 4.12b reduced events negative slopes. The have
Chapter where: Fig. (T), the The apparent 2) tion
L=-
86 QUI, JOABLL (S/uIQ)/X -L <>
Q aul] jeaesy peonpey