Page 102 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 102
85
Models
Interpretation
from
|
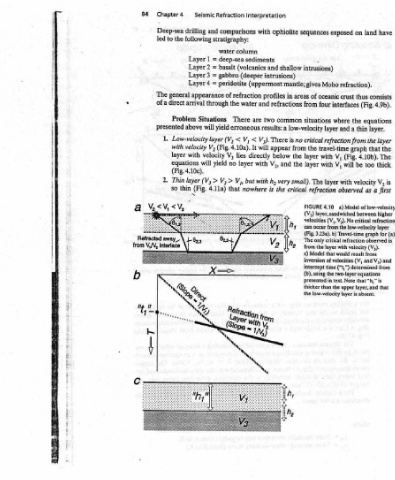
have Model showing velocity a) 4.11 FIGURE layer with depth, but with a thin in (hy very small). b) The first refraction, thin layer, arrives top of the from the the direct arrival, or after the either after refraction (or after both); it may second first refraction to identify the be difficult is If the first refraction on the record. c) overlooked, inversion equations yield a directly over the
land (Fig. 4.9b). equations layer. the that 4.10b). too velocity as a of low-velocity graph observed from and V,) that “h,” is absent.
on refraction). thus the thin a graph be observed Model refraction velocity (V3). (V, (“t,”) determined the two-layer equations upper layer, and
exposed Moho crust oceanic interfaces where and layer critical refraction from travel-time V, (Fig. will V, layer with a) 4.10 layer, sandwiched between velocities (V,, V3). No critical refraction can occur from the low-velocity b) Travel-time the layer with that would result of velocities time in text. Note the low-velocity layer is
sequences ; shallow intrusions) mantle; gives of areas four from situations low-velocity no is the from with layer the with layer the The small). refraction critical FIGURE (V,) (Fig. 3.23a). only critical The from Model ¢) inversion intercept (b), using presented thicker than the
Interpretation ophiolite with sediments and (volcanics intrusions) (deeper (uppermost profiles in and water refractions common two are a results: There V;). < appear will It directly below and V,, with with but very h, the is nowhere
Refraction comparisons water column deep-sea basalt gabbro peridotite of refraction the There yield erroneous V, < (V, 4.10a). (Fig. lies V; layer no yield V), that
Seismic and drilling following stratigraphy: = 1 Layer = Layer 2 Layer 3 = 4 Layer = appearance through arrival Problem Situations will above layer velocity V, velocity will 4.10c). layer (V;>V.,> 4.11a) Fig. / L-6. r
Chapter4 Deep-sea the to led The general direct of a presented 1. Low-velocity with layer with equations (Fig. Thin 2. thin so V5 < < V; vs away ace Int
84 V, . Refracted from V,/V,
a