Page 98 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 98
81
refraction
Models
many
Interpretation
of
inversion
a
2h,cos 0.5
below.
V;
on
,
given
="
2h,cos®,;
is
vi
(Fig. 4,6)
V3
7
Xx
+
&
intercept:
case
T; =
pt:
2.24)
time:
4-layer
(Fig.
:
T-Axis
travel
sequence
top of
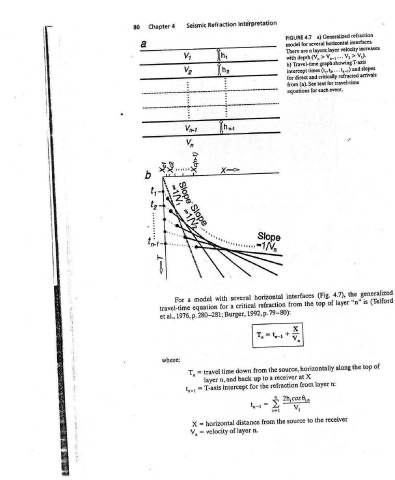
a) Generalized refraction a for Anexample n=l1> Direct Arrival model for several horizontal interfaces. X layers; layer velocity increases v. = time: T, V,)- travel Va-1-+» V2? > 1 b) Travel-time graph showing T-axis intercept: 0 intercept times (t,, t»--- ta-1) and slopes T-Axis for direct and critically refracted arrivals 0, distance: critical from (a). See text for travel-time Refraction Ist n=2=
the
along
FIGURE 4.7 There are n with depth (V, equations for each event. interfaces top the from Vv horizontally source, X at receiver from refraction 8; 2h,cos 2 the to source the
Interpretation horizontal several refraction critical 1992, p. 79-80): the from down toa up back the for 2. » from distance n. layer
Refraction [h with for a p. 280-281; Burger, time travel n, and layer intercept T-axis horizontal of velocity
Seismic Vo model a equation 1976, = T, = t-1 * > i
"
Chapter4 For travel-time al., et where:
a
80
:
!
t