Page 95 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 95
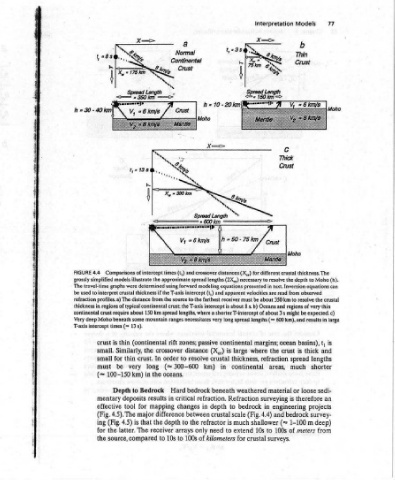
77 Moho (h). resolve the crustal thin large is t, and lengths shorter sedi- an projects survey- deep) from
Models thickness. The to the depth text. Inversion equations can read from observed to regions of very results in 600 km), and basins), thick is spread much loose or therefore is bedrock m 1-100 meters of
Interpretation for different crustal resolve to necessary modeling equations presented in apparent velocities are be about 350 km receiver must Oceans and b) is about 8s. lengths, where a shorter T-intercept of about 3 s might be expected. c) lengths (= long spread ocean margins; continental crust the where large refraction thickness, areas, continental weathered
a Normal Continental re and crossover distances (X,,) times (t,) lengths (2X,,) approximate spread and (t,) if the T-axis intercept the farthest ranges very necessi passive zones; is (X,,) distance crustal resolve to in km) (=300-600 beneath bedrock Hard refraction. critical depth in changes crustal between is refractor the to to need only arrays of kilometers
we * from the source to regions of typical continental crust; the T-axis intercept 150 km spread in rift crossover order oceans. in mapping difference depth receiver 10s to
e the (continental the In long the Bedrock results the
X, 2 Comparisons of intercept models illustrate require about h thin Similarly, thin very Depth deposits tool The 4.5) latter. source, compared
Lo 175k The travel-time graphs were determined using forward thickness m¢ some 13s). crust. in km) to for major that is The
kK to interpret crustal refraction profiles. a) The distance times (+ is crust small. for small be must 100-150 mentary effective 4.5). (Fig. (Fig. the
4.4 grossly simplified continental crust Very deep Moho b intercept (= ing for the
FIGURE used be thickness in T-axis
1 METRE NERO TREY 7 ETT Te RE RTE TRAN AMET REPS
ID
EBT
RO
SUT
Eee
devel- to a - re slopes plot true inter- a shal- will the
was (h), separat- (T) 43e) structure the travel-time the for inversion observed seismic the T-axis from is crust, t, Where
interface depth at travel time a applied Fig. velocity and (t,) the solved following from the utility of The arrival Moho the ranges).
horizontal interface The when graph interpret the time from be then using the cess Mt! of direct of refracted results the 4.4). (Fig. refracted where continental mountain
single, an (V.): is: uations; revel ile to intercept directly can time (h), slope a slope tiV, 0, 2cos that illustrates thickness critically arrival normal-thickness
a from involves velocity source the V,+V, Vv,-V, e modeling sredicied used be The read intercept =>V,= 200 (Zt) AY; a fh model case the time”; the to (collisional
Intérpretation refraction 4.3d) (Fig. higher a from (X) 2hcos 0, Vv, () =! V, 2han@, 2h = forward yield a hand, can (Fig. 4.3a). arrivals. are and A = A 1 V, = sin 0, 2hcos 0, V, inversion the single-layer crustal in “delay compared areas of thick is
Refraction critical model from (V,) distance = intercept angle sin = distance = distance can be they other profile refracted slopes Direct of Refracted t= represents The changes a as of 4.4c), (Fig. relative to crust
Seismic Interface a behind Chapter 3. The velocity horizontal T-axis = ll critical I critical = crossover equations 4.3d), (Fig. the on refraction observed and The observed s Slope Slope of this case, profile (Fig. 4.3a). Thickness method map to thought be delayed is 4.4b). Thus, continental
Chapter4 Horizontal theory The oped in ing lower a receiver at where: t, a » ¢ = X, cr above The model thetical Inversion, an from the direct (Fig. 4.3b,c). equations: in Fig. 4.3d, refraction Crustal refraction can (t,) deep Moho (Fig. large where
76 Single of cept low be