Page 92 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 92
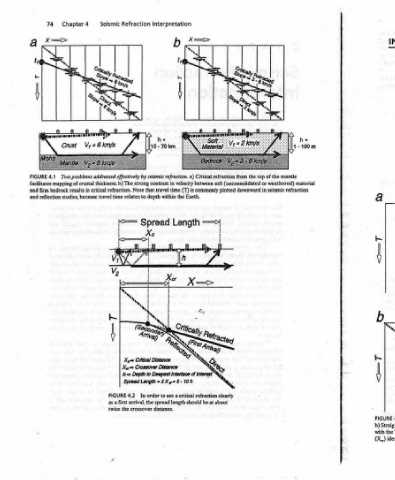
, 75 Models Interpretation MODELS INTERPRETATION for theory The developed is waves seismic of refraction the 3. Chapter in Interpretation identification the involves data refraction of seismic arrivals of linear travel-time on drawn lines of slopes The 4.3). (Fig. plots to relate arrivals through refracted critically and direct by encountered velocities con- with layers For waves. horizont
material or weathered) in seismic refraction
top of the mantle
Critical refraction from the (unconsolidated (T) is commonly plotted downward =—_ be at about
Interpretation a) velocity between soft travel time the Earth. 25+ 10h = 2X In order to see a critical refraction clearly as a first arrival, the spread length should
Refraction Two problems addressed effectively by seismic refraction. thickness. b) The strong contrast in that Spread Length 4.2 the crossover distance.
Seismic and reflection studies, because travel time relates to depth within FIGURE twice
4 firm bedrock results in critical refraction. Note
Chapter 1 C facilitates mapping of crustal
a‘k=> RIOR FIGURE and
74 i 4.1