Page 101 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 101
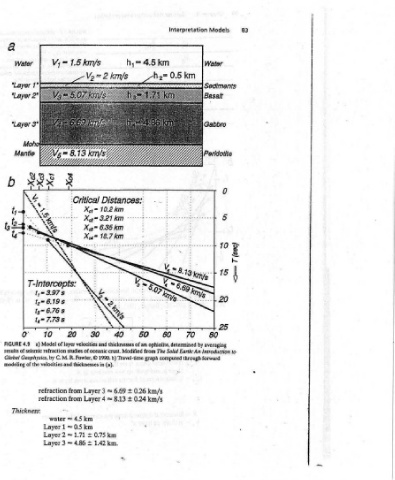
83 to
Models Water Sediments 20 | BS 80 by averaging Introduction forward
Interpretation km 0.5 IS a KEAAREP : ; VS. ieee : : rit 70 The Solid Earth: An _ computed
=45km _h2= oe : ; 60 50 thicknesses of an ophiolite, determined km/s 0.24 km/s ;
h, om penmanns 6.35 km : Ngee. , 40 studies of oceanic crust. Modified from 1990. b) Travel-time graph (a). 0.26 + 6.69 ~ + 8.13 ~ km.
1.5 km/s _-Ve=2km/s = Xcg™ HAR 30 of layer velocities and © thicknesses in 3 Layer from Layer 4 from km 4.5 1~+0.5km 0.75km + 1.71 1.42 + 4.86
= $ 20 ~ ~ 2 ~ 3
V; T-Intercepts: t;=3.97s eBIGg t= 7.738 Model Global Geophysics, by C. M. R. Fowler, refraction refraction water Layer Layer Layer
ts= 6.76 10 a) results of seismic refraction modeling of the velocities and
Water 0 4.9 Thickness:
FIGURE
(km) 30 Exploration Seismology, the from the air firing is the direct arrival. refractions from within Chapters 5 water (see
Distance basin. Modified from A sonobuoy was tossed into the water; the ship then (to the right). The horizontal scale gives the distance the elapsed time between extending through the origin arrivals, are bottom of the
Interpretation Receiver 20 ocean an linear event the record, some as first reflections from the
Refraction to profile recorded in moved away The source (ship) to the receiver (sonobuoy). vertical scale represents
Seismic Source Seismic refraction 2nd ed.. by R. E. Sheriff and L. P. Geldart, © 1995. arrival of events at the sonobuoy. The Linear events observed at greater distances on from the Moho. Hyperbolic events are
Chapter4 oe) S 4.8 periodically fired an air gun as it and
(S) OUI], JEABLL — FIGURE and gun the crust and 6).
82