Page 103 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 103
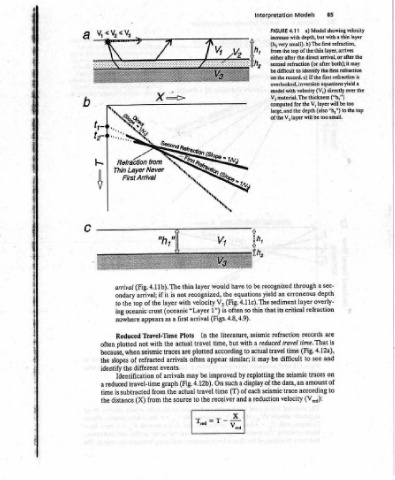
Model showing velocity layer thin layer, arrives first refraction is directly over the layer will be too to the top
85 with depth, but with a thin the direct arrival, or after the refraction (or after both); it may If the first refraction thickness (“h,”) (also “h,”) too small. sec- a depth overly- refraction are is 4.12a), and on of to
Models a) 4.11 (hy very small). b) The first refraction, top of the to identify the overlooked, inversion equations yield a model with velocity (V,) V, for the the depth of the V, layer will be through erroneous layer critical records travel time. That (Fig. time see to difficult traces seismic amount data, an according trace (V,.4): velocity
Interpretation FIGURE in from the either after second be difficult on the record. c) V; material. The computed large, and recognized an yield sediment its that refraction reduced travel be may the seismic reduction
to be equations 4.11c). The thin so seismic a with actual to it replotting a display of the each a
have (Fig. often (Figs. 4.8, 4.9). literature, but similar; by such of (T) and Xx Vis
would the V; is 1”) the time, according appear improved On time receiver 7, =
layer recognized, velocity arrival In travel plotted often be may (Fig. 4.12b). travel the to Trea
= N My, thin not with (oceanic “Layer as a first Plots actual are arrivals actual source
+ is it layer the traces events. arrivals graph the the
x from 4.11b). The if arrival; the of crust appears Travel-Time with seismic refracted different of travel-time from from
GY Refraction Never Layer First Arrival (Fig. arrival ondary top the oceanic nowhere Reduced not plotted of the Identification subtracted (X) distance
‘y Thin to ing because, when slopes identify reduced is
often time
| the a the
have consists layer the The thick is V; first higher layer (a). for is and from that
land (Fig. 4.9b). equations layer. the that 4.10b). too velocity as a of low-velocity graph observed from and V,) that “h,” is absent.
on refraction). thus the thin a graph be observed Model refraction velocity (V3). (V, (“t,”) determined the two-layer equations upper layer, and
exposed Moho crust oceanic interfaces where and layer critical refraction from travel-time V, (Fig. will V, layer with a) 4.10 layer, sandwiched between velocities (V,, V3). No critical refraction can occur from the low-velocity b) Travel-time the layer with that would result of velocities time in text. Note the low-velocity layer is
sequences ; shallow intrusions) mantle; gives of areas four from situations low-velocity no is the from with layer the with layer the The small). refraction critical FIGURE (V,) (Fig. 3.23a). only critical The from Model ¢) inversion intercept (b), using presented thicker than the
Interpretation ophiolite with sediments and (volcanics intrusions) (deeper (uppermost profiles in and water refractions common two are a results: There V;). < appear will It directly below and V,, with with but very h, the is nowhere
Refraction comparisons water column deep-sea basalt gabbro peridotite of refraction the There yield erroneous V, < (V, 4.10a). (Fig. lies V; layer no yield V), that
Seismic and drilling following stratigraphy: = 1 Layer = Layer 2 Layer 3 = 4 Layer = appearance through arrival Problem Situations will above layer velocity V, velocity will 4.10c). layer (V;>V.,> 4.11a) Fig. / L-6. r
Chapter4 Deep-sea the to led The general direct of a presented 1. Low-velocity with layer with equations (Fig. Thin 2. thin so V5 < < V; vs away ace Int
84 V, . Refracted from V,/V,
a