Page 212 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 212
195
Earthquakes
of
Characteristics
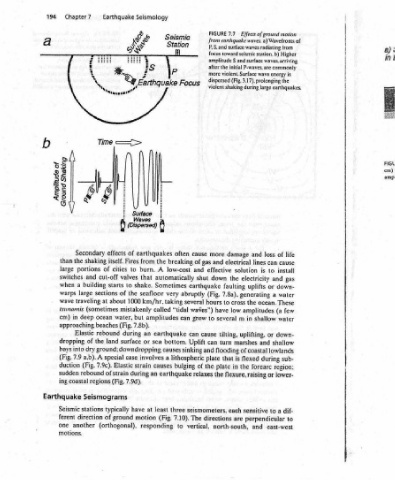
a) ‘ Small Amplitude in Ocean Deep Wave Generates Earthquake “Sy Focus (afew alate causes water wave. Wave is low of seafloor during earthquake offset Tsunami.a) Abrupt 7.8 FIGURE Wave thinner water layer. with sea bottom in shallow area channels energy into Interaction cm) in deep ocean. b) inundating coastal areas. violently) amplitude grows considerably. rapidly (and often After Earthquake
|
Effects of ground motion a) Wavefronts of waves. Higher seismic station. b) S and surface waves, arriving P-waves, are commonly wave energy is prolonging the earthquakes. life of loss and cause can lines install to is and electricity gas or uplifts down- generating water a These ocean. the few (a amplitudes water shallow uplifting. down- or shallow and lowlands sub- during flexed r
7.7 from earthquake waves radiating from surface initial violent. Surface 3.17), (Fig. shaking during large damage electrical solution the faulting 7.8a), cross to low in m several tilting, marshes turn flooding of coastal is that the in flexure, raising each are north-south,
FIGURE P,S. and focus toward amplitude after the more dispersed violent more and of gas effective down shut earthquake (Fig. hours have to cause can and plate plate the relaxes the seismometers, directions
Seismic Station fi P often breaking low-cost automatically Sometimes very taking “tidal earthquake bottom. causes earthquake three 7.10). to
non Focus cause and abruptly several waves”) grow can can Uplift sinking lithospheric of bulging The vertical,
Seismology z Z f Earthquake Surface Waves (Dispersed) earthquakes from the A burn. that shake. seafloor km/hr, called amplitudes but 7.8b). an sea or involves a causes strain an during have least at motion (Fig. responding
Earthquake As i e a et Seon 1 + 1 ' 1 ‘ 1 ‘ i ' ' ' ! ( of effects Fires itself. cities to valves cut-off to starts the of 1000 about mistakenly water, (Fig. during rebound surface land ground: downdropping case special Elastic of strain 7.9d). (Fig. typically ground (orthogonal).
* ‘ * ae shaking of sections at (sometimes ocean beaches the A 7.9c). regions Seismograms of
a i . 5 Secondary portions and building traveling deep of dry a,b). (Fig. rebound stations direction
Chapter? the switches a large tsunamis in approaching Elastic dropping into 7.9 coastal another
buryeys punos than large when warps wave cm) bays (Fig. duction sudden ing Earthquake Seismic ferent one motions.
Jo epnyjdury
194
Q