Page 161 - Fluid Power Engineering
P. 161
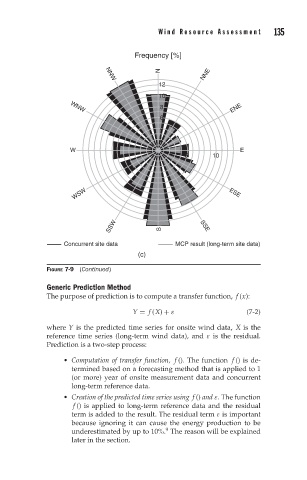
W ind Resource Assessment 135
Frequency [%]
NNE
N
NNW
12
10
ENE
8
WNW
6
4
2
W E
5 10
WSW ESE
SSW S SSE
Concurrent site data MCP result (long-term site data)
(c)
FIGURE 7-9 (Continued)
Generic Prediction Method
The purpose of prediction is to compute a transfer function, f (x):
Y = f (X) + ε (7-2)
where Y is the predicted time series for onsite wind data, X is the
reference time series (long-term wind data), and ε is the residual.
Prediction is a two-step process:
Computation of transfer function, f (). The function f () is de-
termined based on a forecasting method that is applied to 1
(or more) year of onsite measurement data and concurrent
long-term reference data.
Creation of the predicted time series using f () and ε. The function
f () is applied to long-term reference data and the residual
term is added to the result. The residual term ε is important
because ignoring it can cause the energy production to be
9
underestimated by up to 10%. The reason will be explained
later in the section.