Page 78 - Wire Bonding in Microelectronics
P. 78
Bonding W ir e Metallur gy and Characteristics 57
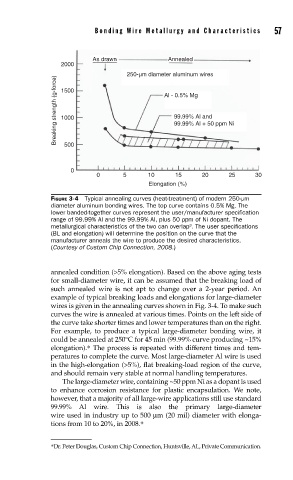
As drawn Annealed
2000
250-µm diameter aluminum wires
Breaking strength (g-force) 1000 Al - 0.5% Mg
1500
99.99% Al and
99.99% Al + 50 ppm Ni
500
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Elongation (%)
FIGURE 3-4 Typical annealing curves (heat-treatment) of modern 250-µm
diameter aluminum bonding wires. The top curve contains 0.5% Mg. The
lower banded-together curves represent the user/manufacturer specifi cation
range of 99.99% Al and the 99.99% Al, plus 50 ppm of Ni dopant. The
metallurgical characteristics of the two can overlap . The user specifi cations
3
(BL and elongation) will determine the position on the curve that the
manufacturer anneals the wire to produce the desired characteristics.
(Courtesy of Custom Chip Connection, 2008.)
annealed condition (>5% elongation). Based on the above aging tests
for small-diameter wire, it can be assumed that the breaking load of
such annealed wire is not apt to change over a 2-year period. An
example of typical breaking loads and elongations for large-diameter
wires is given in the annealing curves shown in Fig. 3-4. To make such
curves the wire is annealed at various times. Points on the left side of
the curve take shorter times and lower temperatures than on the right.
For example, to produce a typical large-diameter bonding wire, it
could be annealed at 250°C for 45 min (99.99% curve producing ~15%
elongation).∗ The process is repeated with different times and tem-
peratures to complete the curve. Most large-diameter Al wire is used
in the high-elongation (>5%), flat breaking-load region of the curve,
and should remain very stable at normal handling temperatures.
The large-diameter wire, containing ~50 ppm Ni as a dopant is used
to enhance corrosion resistance for plastic encapsula tion. We note,
however, that a majority of all large-wire applications still use standard
99.99% Al wire. This is also the primary large-diameter
wire used in industry up to 500 µm (20 mil) diameter with elonga-
tions from 10 to 20%, in 2008.∗
∗Dr. Peter Douglas, Custom Chip Connection, Huntsville, AL, Private Communication.