Page 210 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 210
P2: KVU/KXT
T1: IML
QC: —/—
P1: KVU/KXT
June 22, 2007
AT029-Manual
AT029-04
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
190 CHARACTERIZATION AND PROPERTIES OF PETROLEUM FRACTIONS
properties of such mixtures. Application of this approach is
in Example 4.16.
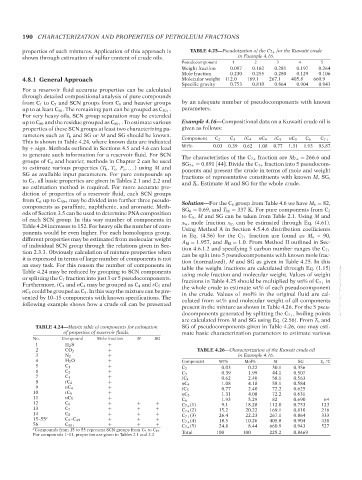
shown through estimation of sulfur content of crude oils. 21:30 TABLE 4.25—Pseudoization of the C 7+ for the Kuwaiti crude
Pseudocomponent 1 2 3 4 5
Weight fraction 0.097 0.162 0.281 0.197 0.264
Mole fraction 0.230 0.255 0.280 0.129 0.106
4.8.1 General Approach Molecular weight 112.0 169.1 267.1 405.8 660.9
Specific gravity 0.753 0.810 0.864 0.904 0.943
For a reservoir fluid accurate properties can be calculated
through detailed compositional analysis of pure compounds
from C 1 to C 5 and SCN groups from C 6 and heavier groups by an adequate number of pseudocomponents with known
up to at least C 50 . The remaining part can be grouped as C 50+ . parameters.
For very heavy oils, SCN group separation may be extended
up to C 80 and the residue grouped as C 80+ . To estimate various Example 4.16—Compositional data on a Kuwaiti crude oil is
properties of these SCN groups at least two characterizing pa- given as follows:
rameters such as T b and SG or M and SG should be known. Component
This is shown in Table 4.24, where known data are indicated C 2 C 3 iC 4 nC 4 iC 5 nC 5 C 6 C 7+
by + sign. Methods outlined in Sections 4.5 and 4.6 can lead Wt% 0.03 0.39 0.62 1.08 0.77 1.31 1.93 93.87
to generate such information for a reservoir fluid. For SCN The characteristics of the C 7+ fraction are M 7+ = 266.6 and
groups of C 6 and heavier, methods in Chapter 2 can be used SG 7+ = 0.891 [44]. Divide the C 7+ fraction into 5 pseudocom-
to estimate various properties (T b , T c , P c ,...) using M and ponents and present the crude in terms of mole and weight
SG as available input parameters. For pure compounds up fractions of representative constituents with known M, SG,
to C 5 , all basic properties are given in Tables 2.1 and 2.2 and and T b . Estimate M and SG for the whole crude.
no estimation method is required. For more accurate pre-
diction of properties of a reservoir fluid, each SCN groups
from C 6 up to C 50+ may be divided into further three pseudo- Solution—For the C 6 group from Table 4.6 we have M 6 = 82,
components as paraffinic, naphthenic, and aromatic. Meth-
SG 6 = 0.69, and T b6 = 337 K. For pure components from C 2
ods of Section 3.5 can be used to determine PNA composition to C 5 , M and SG can be taken from Table 2.1. Using M and
of each SCN group. In this way number of components in x w , mole fraction x m can be estimated through Eq. (4.61).
Table 4.24 increases to 152. For heavy oils the number of com- Using Method A in Section 4.5.4.6 distribution coefficients
ponents would be even higher. For each homologous group, in Eq. (4.56) for the C 7+ fraction are found as M o = 90,
different properties may be estimated from molecular weight A M = 1.957, and B M = 1.0. From Method II outlined in Sec-
of individual SCN group through the relations given in Sec-
tion 2.3.3. Obviously calculation of mixture properties when tion 4.6.1.2 and specifying 5 carbon number ranges the C 7+
can be split into 5 pseudocomponents with known mole frac-
it is expressed in terms of large number of components is not tion (normalized), M and SG as given in Table 4.25. In this
an easy task. For this reason the number of components in table the weight fractions are calculated through Eq. (1.15)
Table 4.24 may be reduced by grouping to SCN components using mole fraction and molecular weight. Values of weight
or splitting the C 7 fraction into just 3 or 5 pseudocomponents. fractions in Table 4.25 should be multiplied by wt% of C 7+ in
Furthermore, iC 4 and nC 4 may be grouped as C 4 and iC 5 and the whole crude to estimate wt% of each pseudocomponent
nC 5 could be grouped as C 5 . In this way the mixture can be pre- in the crude. Values of mol% in the original fluid are cal- --`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
sented by 10–15 components with known specifications. The culated from wt% and molecular weight of all components
following example shows how a crude oil can be presented
present in the mixture as shown in Table 4.26. For the 5 pseu-
docomponents generated by splitting the C 7+ , boiling points
are calculated from M and SG using Eq. (2.56). From T b and
TABLE 4.24—Matrix table of components for estimation SG of pseudocomponents given in Table 4.26, one may esti-
of properties of reservoir fluids. mate basic characterization parameters to estimate various
No. Compound Mole fraction M SG
1 H 2 S +
2 CO 2 + TABLE 4.26—Characterization of the Kuwait crude oil
3 N 2 + in Example 4.16.
4 H 2 O + Component Wt% Mol% M SG T b , C
◦
5 C 1 +
C 2 0.03 0.22 30.1 0.356
6 C 2 +
C 3 0.39 1.99 44.1 0.507
7 C 3 + iC 4 0.62 2.40 58.1 0.563
8 iC 4 + nC 4 1.08 4.18 58.1 0.584
9 nC 4 + iC 5 0.77 2.40 72.2 0.625
10 iC 5 + nC 5 1.31 4.08 72.2 0.631
11 nC 5 + C 6 1.93 5.29 82 0.690 64
12 C 6 + + + C 7+ (1) 9.1 18.28 112.0 0.753 123
13 C 7 + + + C 7+ (2) 15.2 20.22 169.1 0.810 216
14 C 8 + + + C 7+ (3) 26.4 22.23 267.1 0.864 333
15–55 a C 9 –C 49 + + + C 7+ (4) 18.5 10.26 405.8 0.904 438
56 C 50+ + + + C 7+ (5) 24.8 8.44 660.9 0.943 527
a Compounds from 15 to 55 represent SCN groups from C 9 to C 49 .
For compounds 1–11, properties are given in Tables 2.1 and 2.2. Total 100 100 225.2 0.8469
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT