Page 158 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 158
P2: IML/FFX
T1: IML
QC: IML/FFX
P1: IML/FFX
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
14:23
June 22, 2007
AT029-Manual
AT029-03
138 CHARACTERIZATION AND PROPERTIES OF PETROLEUM FRACTIONS
lation. Calculated number is called calculated cetane index
(CCI) and can be determined from the following relation:
CCI = 454.74 − 1641.416SG + 774.74SG 2
(3.129) − 0.554T 50 + 97.083(log T 50 ) 2
10
where T 50 is the ASTM D 86 temperature at 50% point in C.
◦
Another characteristic of diesel fuels is called diesel index (DI)
Calculated Aniline Point, °C (3.130) DI = (API)(1.8AP + 32) ◦
defined as:
100
which is a function of API gravity and aniline point in C.
Cetane index is empirically correlated to DI and AP in the
following form [24]:
(3.131) CI = 0.72DI + 10
(3.132) CI = AP − 15.5
where AP is in C. Calculated cetane index (CI) is also related
◦
to n-paraffin content (%NP) of diesel fuels in the following
from [87].
Experimental Aniline Point, °C
(3.133) %NP = 1.45CI − 57.5
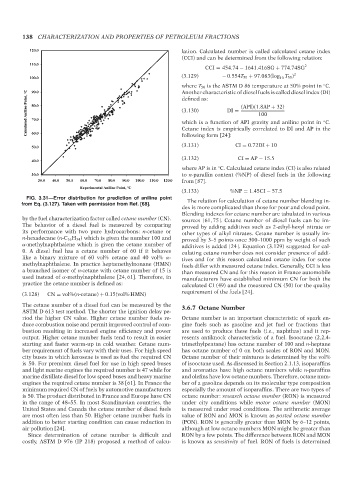
FIG. 3.31—Error distribution for prediction of aniline point The relation for calculation of cetane number blending in-
from Eq. (3.127). Taken with permission from Ref. [68].
dex is more complicated than those for pour and cloud point.
Blending indexes for cetane number are tabulated in various
by the fuel characterization factor called cetane number (CN). sources [61, 75]. Cetane number of diesel fuels can be im-
The behavior of a diesel fuel is measured by comparing proved by adding additives such as 2-ethyl-hexyl nitrate or
its performance with two pure hydrocarbons: n-cetane or other types of alkyl nitrates. Cetane number is usually im-
n-hexadecane (n-C 16 H 34 ) which is given the number 100 and proved by 3–5 points once 300–1000 ppm by weight of such
α-methylnaphthalene which is given the cetane number of additives is added [24]. Equation (3.129) suggested for cal-
0. A diesel fuel has a cetane number of 60 if it behaves culating cetane number does not consider presence of addi-
like a binary mixture of 60 vol% cetane and 40 vol% α- tives and for this reason calculated cetane index for some
methylnaphthalene. In practice heptamethylnonane (HMN) fuels differ with measured cetane index. Generally, CCI is less
a branched isomer of n-cetane with cetane number of 15 is than measured CN and for this reason in France automobile
used instead of α-methylnaphthalene [24, 61]. Therefore, in manufacturers have established minimum CN for both the
practice the cetane number is defined as: calculated CI (49) and the measured CN (50) for the quality
requirement of the fuels [24].
(3.128) CN = vol%(n-cetane) + 0.15(vol% HMN)
The cetane number of a diesel fuel can be measured by the 3.6.7 Octane Number
ASTM D 613 test method. The shorter the ignition delay pe-
riod the higher CN value. Higher cetane number fuels re- Octane number is an important characteristic of spark en-
duce combustion noise and permit improved control of com- gine fuels such as gasoline and jet fuel or fractions that
bustion resulting in increased engine efficiency and power are used to produce these fuels (i.e., naphthas) and it rep-
output. Higher cetane number fuels tend to result in easier resents antiknock characteristic of a fuel. Isooctane (2,2,4-
starting and faster warm-up in cold weather. Cetane num- trimethylpentane) has octane number of 100 and n-heptane
ber requirement of fuels vary with their uses. For high speed has octane number of 0 on both scales of RON and MON.
city buses in which kerosene is used as fuel the required CN Octane number of their mixtures is determined by the vol%
is 50. For premium diesel fuel for use in high speed buses of isooctane used. As discussed in Section 2.1.13, isoparaffins
and light marine engines the required number is 47 while for and aromatics have high octane numbers while n-paraffins
marine distillate diesel for low speed buses and heavy marine and olefins have low octane numbers. Therefore, octane num-
engines the required cetane number is 38 [61]. In France the ber of a gasoline depends on its molecular type composition
minimum required CN of fuels by automotive manufacturers especially the amount of isoparaffins. There are two types of
is 50. The product distributed in France and Europe have CN octane number: research octane number (RON) is measured
in the range of 48–55. In most Scandinavian countries, the under city conditions while motor octane number (MON)
United States and Canada the cetane number of diesel fuels is measured under road conditions. The arithmetic average
are most often less than 50. Higher cetane number fuels in value of RON and MON is known as posted octane number
addition to better starting condition can cause reduction in (PON). RON is generally greater than MON by 6–12 points,
air pollution [24]. although at low octane numbers MON might be greater than
Since determination of cetane number is difficult and RON by a few points. The difference between RON and MON
costly, ASTM D 976 (IP 218) proposed a method of calcu- is known as sensitivity of fuel. RON of fuels is determined
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT