Page 208 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 208
QC: —/—
T1: IML
P2: KVU/KXT
P1: KVU/KXT
AT029-Manual
21:30
June 22, 2007
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
AT029-04
188 CHARACTERIZATION AND PROPERTIES OF PETROLEUM FRACTIONS
V
where f (T) is the fugacity of a specie in the vapor phase
s
fugacity coefficient ϕ(T, T , p) for components with boiling
whose boiling point is T. When T = T o the above equation is gas the left-hand side of Eq. (4.114) should be multiplied by
s
applied to the lightest component in the mixture and when point T at temperature T and pressure p. These thermody-
T =∞ it is applied to the last and heaviest component whose namic properties are defined in Chapter 6 and can be obtained
boiling point may be considered as infinity. For simplicity it is from an equation of state for hydrocarbon systems. A more
assumed that the vapor phase is ideal gas and the liquid phase general form of Eq. (4.114) for high-pressure VLE calcula-
is an ideal solution. Under such conditions Eq. (4.110) for a tions is in terms equilibrium ratio can be written as
component with boiling point T in a mixture can be written
as (4.115) F = F × K T
V
L
T
T
(4.111) dy T p = dx T p T s
where K T is the equilibrium ratio for a component with boil-
where dy T is the mole fraction of a component having boil- ing point T at temperature T and pressure p. As it will be
s
ing point T in the vapor phase and dx T is the mole fraction shown in Chapter 6, K T depends on vapor pressure p .
s
of the same component in the liquid phase. p T s is the satura- Now we apply the above equations for design and operation
tion pressure (or vapor pressure) of components with boiling of a separation unit for flash distillation of reservoir fluids
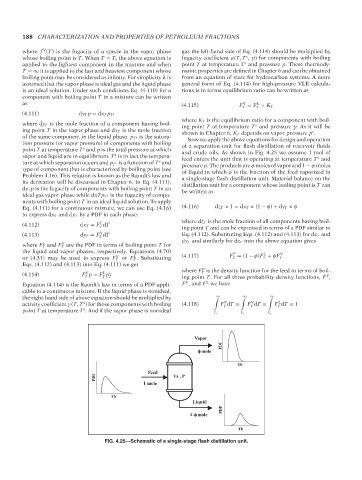
point T at temperature T and p is the total pressure at which and crude oils. As shown in Fig. 4.25 we assume 1 mol of
s
vapor and liquid are in equilibrium. T is in fact the tempera- feed enters the unit that is operating at temperature T and
s
s
s
ture at which separation occurs and p T s is a function of T and pressure p. The products are φ moles of vapor and 1 − φ moles
type of component that is characterized by boiling point (see of liquid in which φ is the fraction of the feed vaporized in
Problem 4.16). This relation is known as the Raoult’s law and a single-stage flash distillation unit. Material balance on the
its derivation will be discussed in Chapter 6. In Eq. (4.111), distillation unit for a component whose boiling point is T can
dy T p is the fugacity of components with boiling point T in an be written as
ideal gas vapor phase while dxTp T s is the fugacity of compo-
nents with boiling point T in an ideal liquid solution. To apply
Eq. (4.111) for a continuous mixture, we can use Eq. (4.16) (4.116) dz T × 1 = dx T × (1 − φ) + dy T × φ
to express dx T and dy T by a PDF in each phase:
where dz T is the mole fraction of all components having boil-
L
(4.112) dx T = F dT ing point T and can be expressed in terms of a PDF similar to
T
V
(4.113) dy T = F dT Eq. (4.112). Substituting Eqs. (4.112) and (4.113) for dx T and
T
dy T and similarly for dz T into the above equation gives
V
L
where F and F are the PDF in terms of boiling point T for
T
T
the liquid and vapor phases, respectively. Equations (4.70) F L V
L
or (4.31) may be used to express F V or F . Substituting (4.117) F = (1 − φ)F + φF T
T
T
T T
Eqs. (4.112) and (4.113) into Eq. (4.111) we get
F
where F is the density function for the feed in terms of boil-
T
V
L
(4.114) F p = F p s T ing point T. For all three probability density functions, F ,
F
T
T
V
L
Equation (4.114) is the Raoult’s law in terms of a PDF appli- F , and F we have
cable to a continuous mixture. If the liquid phase is nonideal,
the right-hand side of above equation should be multiplied by ∞ ∞ ∞
V
s
F
L
activity coefficient γ (T, T ) for those components with boiling (4.118) F dT = F dT = F dT = 1
T
T
T
s
point T at temperature T . And if the vapor phase is nonideal
T ◦ T ◦ T ◦
Vapor
PDF
mole
Tb
Feed
PDF Ts , P
mole
Tb
Liquid
PDF
- mole
Tb
FIG. 4.25—Schematic of a single-stage flash distillation unit.
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT