Page 267 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 267
T1: IML
P1: KVU/KXT
AT029-Manual
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
20:46
AT029-06
6. THERMODYNAMIC RELATIONS FOR PROPERTY ESTIMATIONS 247
3
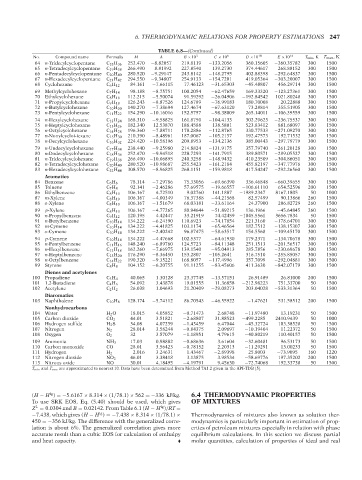
No. P2: KVU/KXT QC: —/— Formula June 22, 2007 TABLE 6.8—(Continued) C × 10 6 D ×10 10 E ×10 14 T min ,K T max ,K
Compound name
B ×10
A
M
64 n-Tridecylcyclopentane C 18 H 36 252.470 −8.82057 219.8119 −133.2056 360.15605 −260.35782 300 1500
65 n-Tetradecylcyclopentane C 19 H 38 266.490 −8.81992 227.8540 −139.2730 374.44617 −268.88152 300 1500
66 n-Pentadecylcyclopentane C 20 H 40 280.520 −9.29147 243.8142 −148.2795 402.88398 −292.64837 300 1500
67 n-Hexadecylcyclopentane C 21 H 42 294.550 −9.34807 254.9133 −154.7201 419.05364 −303.20007 300 1500
68 Cyclohexane C 6 H 12 84.161 −7.66115 77.46123 −31.65303 −45.48807 456.29714 300 1500
69 Methylcyclohexane C 7 H 14 98.188 −8.75751 100.2054 −62.47659 169.33320 −123.27361 300 1500
70 Ethylcyclohexane C 8 H 16 112.215 −5.50074 91.59292 −26.04906 −192.84542 1021.80248 300 1500
71 n-Propylcyclohexane C 9 H 18 126.243 −8.87526 124.6789 −76.99183 180.70008 20.22888 300 1500
72 n-Butylcyclohexane C 10 H 20 140.270 −7.38694 127.4674 −67.63120 73.28814 355.51905 300 1500
73 n-Pentylcyclohexane C 11 H 22 154.290 −10.16016 152.5757 −98.38009 265.14011 −106.39559 300 1500
74 n-Hexylcyclohexane C 12 H 24 168.310 −9.58825 161.8750 −104.4133 302.29623 −236.75537 300 1500
75 n-Heptylcyclohexane C 13 H 26 182.340 −12.53870 188.4588 −138.5801 523.83412 −881.68097 300 1500
76 n-Octylcyclohexane C 14 H 28 196.360 −7.88711 178.2886 −112.8765 330.77533 −271.09270 300 1500
77 n-Nonylcycloi-iexane C 15 H 30 210.390 −8.48961 187.0067 −105.2157 192.47573 192.71532 300 1500
78 n-Decylcyclohexane C 16 H 32 224.420 −10.58196 209.8953 −134.2136 385.00443 −297.79779 300 1500
79 n-Undecylcyclohexane C 17 H 34 238.440 −9.25980 214.8824 −131.9175 357.79740 −261.20128 300 1500
80 n-Dodecylcyclohexane C 18 H 36 252.470 −9.94518 228.7293 −141.7915 389.80571 −289.05527 300 1500
81 n-Tridecylcyclohexane C 19 H 38 266.490 −10.06895 240.3258 −148.9432 410.23509 −304.86051 300 1500
82 n-Tetradecylcyclohexane C 20 H 40 280.520 −10.98687 255.5423 −161.2184 455.82197 −347.77976 300 1500
83 n-Hexadecylcyclohexane C 22 H 44 308.570 −8.96825 268.1151 −159.9818 417.54247 −292.26560 300 1500
Aromatics
84 Benzene C 6 H 6 78.114 −7.29786 75.33056 −69.66390 336.46848 −660.39655 300 1500
85 Toluene C 7 H 8 92.141 −2.46286 57.69575 −19.66557 −106.61110 654.52596 200 1500
86 Ethylbenzene C 8 H 10 106.167 4.72510 9.02760 141.1887 −1989.2347 8167.1805 50 1000
87 m-Xylene C 8 H 10 106.167 −4.00149 76.37388 −44.21568 82.57499 90.13866 260 1500
88 o-Xylene C 8 H 10 106.167 −1.51679 68.03181 −33.61164 24.37900 206.82729 260 1500
89 p-Xylene C 8 H 10 106.167 −4.77265 80.94644 −51.89215 136.1966 −45.64845 260 1500
90 n-Propylbenzene C 9 H 12 120.195 4.42447 33.21919 74.42459 −1045.5561 3656.7834 50 1500
91 n-Butylbenzene C 10 H 14 134.222 −6.24190 110.6923 −74.17854 221.3160 −178.64701 300 1500
92 m-Cymene C 10 H 14 134.222 −4.41825 103.1174 −65.46564 182.7512 −138.15307 300 1500
93 o-Cymene C 10 H 14 134.222 −2.40242 96.87475 −58.63517 154.5568 −109.45170 300 1500
94 p-Cymene C 10 H 14 134.222 −4.47668 102.5377 −64.61930 179.2371 −134.70678 300 1500
95 n-Pentylbenzene C 11 H 16 148.240 −6.89760 124.5723 −84.11348 251.1513 −201.56517 300 1500
96 n-Hexylbenzene C 12 H 18 162.260 −7.66975 139.1540 −95.04913 285.7856 −230.69678 300 1500
97 n-Heptylbenzene C 13 H 20 176.290 −8.36450 153.2807 −105.2641 316.7510 −255.85057 300 1500
98 n-Octylbenzene C 14 H 22 190.320 −9.35221 168.8057 −117.4996 357.7099 −292.04881 300 1500
99 Styrene C 8 H 8 104.152 −6.20755 91.11255 −83.45606 411.3630 −842.07179 300 1500
Dienes and acetylenes
100 Propadiene C 3 H 4 40.065 1.30128 23.37745 −13.57151 26.91489 26.81000 200 1500
101 1,2-Butadiene C 4 H 6 54.092 3.43878 19.01555 11.36858 −212.98223 751.33700 50 1500
102 Acetylene C 2 H 2 26.038 1.04693 21.20409 −29.08273 203.04028 −533.31364 50 1500
Diaromatics
103 Naphthalene C 10 H 8 128.174 −5.74112 86.70543 −46.55922 −1.47621 531.58512 200 1500
Nonhydrocarbons
104 Water H 2 O 18.015 4.05852 −0.71473 2.68748 −11.97480 13.19231 50 1500
105 Carbon dioxide CO 2 44.01 3.51821 −2.68807 31.88523 −499.2285 2410.9439 50 1000
106 Hydrogen sulfide H 2 S 34.08 4.07259 −1.43459 6.47044 −45.32724 103.38528 50 1500
107 Nitrogen N 2 28.014 3.58244 −0.84375 2.09697 −10.19404 11.22372 50 1500
108 Oxygen O 2 32 3.57079 −1.18951 4.79615 −40.80219 110.40157 50 1500
109 Ammonia NH 3 17.03 0.98882 −0.68636 3.61604 −32.60481 96.53173 50 1500
110 Carbon monoxide CO 28.01 3.56423 −0.78152 2.20313 −11.29291 13.00233 50 1500
111 Hydrogen H 2 2.016 3.24631 1.43467 −2.89398 25.8003 −73.9095 160 1220
112 Nitrogen dioxide NO 2 46.01 3.38418 3.13875 3.98534 −58.69776 197.35202 200 1500
113 Nitrous oxide NO 30.01 4.18495 −4.19791 9.45630 −72.74068 192.33738 50 1500
T min and T max are approximated to nearest 10. Data have been determined from Method 7A1.2 given in the API-TDB [5].
ig
(H − H ) =−5.6167 × 8.314 × (1/78.1) × 562 =−336 kJ/kg. 6.4 THERMODYNAMIC PROPERTIES
To use SRK EOS, Eq. (5.40) should be used, which gives OF MIXTURES
L ig
Z = 0.0304 and B = 0.02142. From Table 6.1 (H − H )/RT =
ig
−7.438, which gives (H − H ) =−7.438 × 8.314 × (1/78.1) × Thermodynamics of mixtures also known as solution ther-
450 =−356 kJ/kg. The difference with the generalized corre- modynamics is particularly important in estimation of prop-
lation is about 6%. The generalized correlation gives more erties of petroleum mixtures especially in relation with phase
accurate result than a cubic EOS for calculation of enthalpy equilibrium calculations. In this section we discuss partial
and heat capacity. molar quantities, calculation of properties of ideal and real
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT