Page 135 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 135
136 Chapter 4 Mechanical Testing: Tension Test and Other Basic Tests
(a)
500
σ = 395 MPa
u
400
σ, Stress, MPa 300
200
= 0.366
ε f
AISI 1020 HR Steel
σ f = 266.8 MPa
100
fracture
0
0.00 0.08 0.16 0.24 0.32 0.40
ε, Strain
(b)
400
σ = 201,200ε σ = 264 MPa
o
300 (0.00700, 267.6)
σ, Stress, MPa 200
100 AISI 1020 HR Steel
0.002
(0.00567, 0)
0
0.000 0.003 0.006 0.009 0.012
ε ε, Strain
ε p e
Figure E4.1
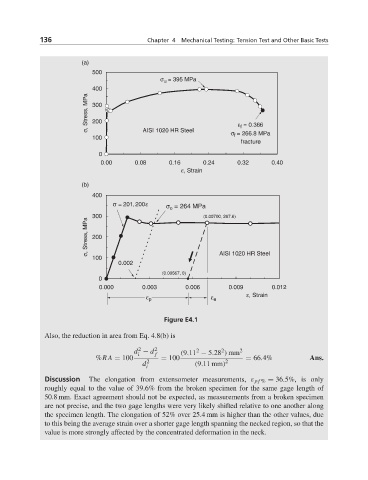
Also, the reduction in area from Eq. 4.8(b) is
2
2
2
d − d 2 f (9.11 − 5.28 ) mm 2
i
%RA = 100 2 = 100 2 = 66.4% Ans.
d (9.11 mm)
i
Discussion The elongation from extensometer measurements, ε pf % = 36.5%, is only
roughly equal to the value of 39.6% from the broken specimen for the same gage length of
50.8 mm. Exact agreement should not be expected, as measurements from a broken specimen
are not precise, and the two gage lengths were very likely shifted relative to one another along
the specimen length. The elongation of 52% over 25.4 mm is higher than the other values, due
to this being the average strain over a shorter gage length spanning the necked region, so that the
value is more strongly affected by the concentrated deformation in the neck.