Page 184 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 184
170 Refrigeration, air conditioning and ventilation
inspection port tubjng
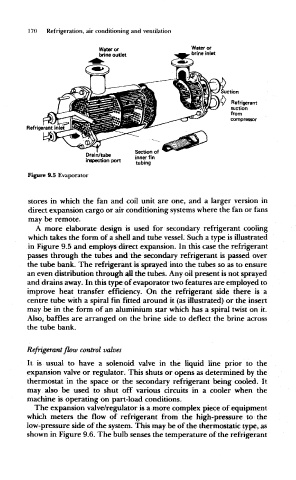
Figure 9.5 Evaporator
stores in which the fan and coil unit are one, and a larger version in
direct expansion cargo or air conditioning systems where the fan or fans
may be remote.
A more elaborate design is used for secondary refrigerant cooling
which takes the form of a shell and tube vessel. Such a type is illustrated
in Figure 9.5 and employs direct expansion. In this case the refrigerant
passes through the tubes and the secondary refrigerant is passed over
the tube bank. The refrigerant is sprayed into the tubes so as to ensure
an even distribution through all the tubes. Any oil present is not sprayed
and drains away. In this type of evaporator two features are employed to
improve heat transfer efficiency. On the refrigerant side there is a
centre tube with a spiral fin fitted around it (as illustrated) or the insert
may be in the form of an aluminium star which has a spiral twist on it.
Also, baffles are arranged on the brine side to deflect the brine across
the tube bank.
Refrigerant flow control valves
It is usual to have a solenoid valve in the liquid line prior to the
expansion valve or regulator. This shuts or opens as determined by the
thermostat in the space or the secondary refrigerant being cooled. It
may also be used to shut off various circuits in a cooler when the
machine is operating on part-load conditions.
The expansion valve/regulator is a more complex piece of equipment
which meters the flow of refrigerant from the high-pressure to the
low-pressure side of the system. This may be of the thermostatic type, as
shown in Figure 9.6. The bulb senses the temperature of the refrigerant