Page 185 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 185
Refrigeration, air conditioning and ventilation 17!
BuJb*
Capillary tube
Tube and space
filled with (c. i Vapour to
Diaphragm
refrigerant I compressor
(c
Criftce
"V"
Liquid from
condenser Evaporator
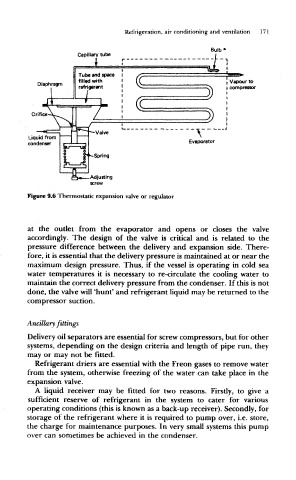
Figure 9.6 Therrnostatic expansion valve or regulator
at the outlet from the evaporator and opens or closes the valve
accordingly. The design of the valve is critical and is related to the
pressure difference between the delivery and expansion side. There-
fore, it is essential that the delivery pressure is maintained at or near the
maximum design pressure. Thus, if the vessel is operating in cold sea
water temperatures it is necessary to re-circulate the cooling water to
maintain the correct delivery pressure from the condenser. If this is not
done, the valve will 'hunt' and refrigerant liquid may be returned to the
compressor suction.
Ancillary fittings
Delivery oil separators are essential for screw compressors, but for other
systems, depending on the design criteria and length of pipe run, they
may or may not be fitted.
Refrigerant driers are essential with the Freon gases to remove water
from the system, otherwise freezing of the water can take place in the
expansion valve.
A liquid receiver may be fitted for two reasons. Firstly, to give a
sufficient reserve of refrigerant in the system to cater for various
operating conditions (this is known as a back-up receiver). Secondly, for
storage of the refrigerant where it is required to pump over, i.e. store,
the charge for maintenance purposes. In very small systems this pump
over can sometimes be achieved in the condenser.