Page 196 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 196
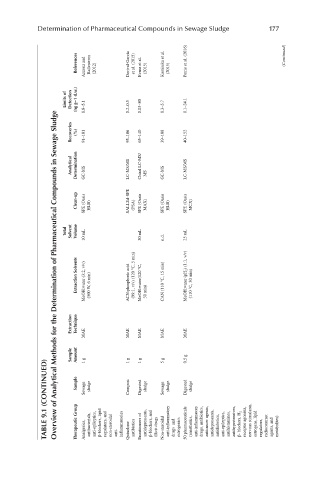
Determination of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Sewage Sludge 177
References Azzouz and Ballesteros (2012) Dorival-García et al. (2015) Evans et al. (2015) Kumirska et al. (2015) Petrie et al. (2016) (Continued)
Limits of Detection (ng g−1 d.w.) 0.8–5.1 0.2–0.5 0.03–80 0.3–5.7 0.1–24.1
Overview of Analytical Methods for the Determination of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Sewage Sludge
Recoveries (%) 91–101 95–106 65–140 39–108 40–152
Analytical Determination GC-MS LC-MS/MS Chiral LC-MS/ MS GC-MS LC-MS/MS
Clean-up SPE (Oasis HLB) SALLEd-SPE (PSA) SPE (Oasis MAX) SPE (Oasis HLB) SPE (Oasis MCX)
Total Solvent Volume 10 mL 30 mL n.d. 25 mL
Extraction Solvents MeOH:water (3:2, v/v) (500 W, 6 min) ACN:phosphoric acid (99:1, v/v) (120 °C, 5 min) MeOH:water(120 °C, 30 min) CAN (110 °C, 15 min) MeOH:water (pH 2 ) (1:1, v/v) (110 °C, 30 min)
Extraction Technique MAE MAE MAE MAE MAE
Sample Amount 1 g 1 g 1 g 5 g 0.5 g
TABLE 9.1 (CONTINUED) Sample Therapeutic Group Sewage Analgesics, sludge antibacterials, anti-epileptics, β-blockers, lipid regulators, and non-steroidal anti- inflammatories Compost Quinolone antibiotics Digested Enantiomers of sludge antidepressants, β-blockers, and illicit drugs Sewage Non-steroidal sl