Page 197 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 197
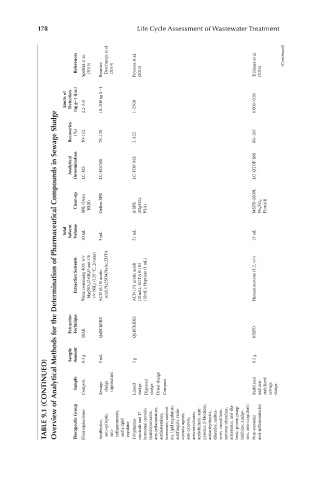
178 Life Cycle Assessment of Wastewater Treatment
References Speltini et al. (2015) Bourdat- Deschamps et al. (2014) Peysson et al. (2013) Triñanes et al. (2016) (Continued)
Limits of Detection (ng g−1 d.w.) 2.2–3.0 10–200 ng L−1 1–2500 0.005–0.05
Overview of Analytical Methods for the Determination of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Sewage Sludge
Recoveries (%) 70–112 78–120 2–122 86–105
Analytical Determination LC-MS LC-MS/MS LC-TOF-MS LC-QTOF-MS
Clean-up SPE (Oasis HLB) Online SPE d-SPE (MgSO4, PSA) MSPD (KOH, Na 2 SO 4 , Florisil)
Total Solvent Volume 10 mL 5 mL 21 mL 15 mL
Extraction Solvents Water containing 40% w/v Mg(NO 3 )2·6H 2 O and 4% v/v NH 3 ) (135 °C, 20 min) ACN (0.1% acetic acid),Na2SO4,NaAc,EDTA ACN (1% acetic acid) (10 mL); EDTA 0.1 M (10mL); Heptane (1 mL) Hexane:acetone (1:2, v/v)
Extraction Technique MAE QuEChERS QuEChERS MSPD
Sample Amount 0.3 g 5 mL 2 g 0.2 g
TABLE 9.1 (CONTINUED) Sample Therapeutic Group Compost Fluoroquinolones Sewage Antibiotics, sludge anti-epileptic, supernatant anti- inflammatories, and a lipid regulator Limed 119 pharma- sludge ceuticals and 17 hormonal steroids Digested (antidepressants, sludge anti-inflammatory, Dried sludge antihistami