Page 247 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 247
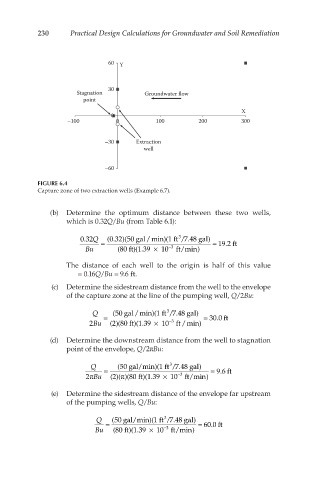
230 Practical Design Calculations for Groundwater and Soil Remediation
60 Y
30
Stagnation Groundwater ow
point
X
0
–100 0 100 200 300
–30 Extraction
well
–60
FIGURE 6.4
Capture zone of two extraction wells (Example 6.7).
(b) Determine the optimum distance between these two wells,
which is 0.32Q/Bu (from Table 6.1):
3
0.32Q = (0.32)(50 gal/min)(1 ft /7.48 gal) = 19.2 ft
Bu (80ft)(1.39 × 10 −3 ft/min)
The distance of each well to the origin is half of this value
= 0.16Q/Bu = 9.6 ft.
(c) Determine the sidestream distance from the well to the envelope
of the capture zone at the line of the pumping well, Q/2Bu:
3
Q = (50gal/min)(1 ft /7.48 gal) = 30.0 ft
−3
2Bu (2)(80ft)(1.39 × 10 ft/min)
(d) Determine the downstream distance from the well to stagnation
point of the envelope, Q/2πBu:
3
Q = (50gal/min)(1 ft /7.48 gal) = 9.6 ft
−3
2 πBu (2)( π)(80ft)(1.39 × 10 ft/min)
(e) Determine the sidestream distance of the envelope far upstream
of the pumping wells, Q/Bu:
3
Q = (50gal/min)(1 ft /7.48 gal) = 60.0 ft
−3
Bu (80ft)(1.39 × 10 ft/min)