Page 127 -
P. 127
6.18 CHAPTER SIX
TABLE 6.6 Flocculation Design Criteria
Process G, s- 1 Detention time, s Gt
Distribution channels 100 to 150 Varies --
mixer to flocculator
High-energy flocculation 20 to 75 900 to 1,500 40,000 to 75,000
for direct filtration
Conventional flocculation 10 to 60 1,000 to 1,500 30,000 to 60,000
(presettling)
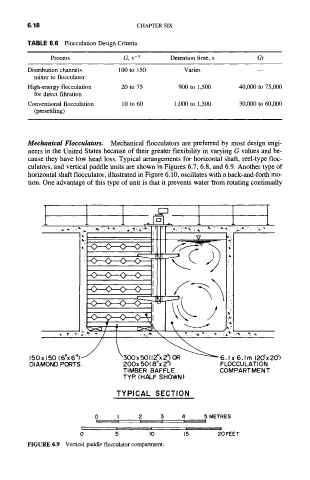
Mechanical Flocculators. Mechanical flocculators are preferred by most design engi-
neers in the United States because of their greater flexibility in varying G values and be-
cause they have low head loss. Typical arrangements for horizontal shaft, reel-type floc-
culators, and vertical paddle units are shown in Figures 6.7, 6.8, and 6.9. Another type of
horizontal shaft flocculator, illustrated in Figure 6.10, oscillates with a back-and-forth mo-
tion. One advantage of this type of unit is that it prevents water from rotating continually
I.l.n/m\
150x 150 16"x 6"1 " ~ ~300xSOl12''x~6.1 x 6.1m (20'x 20')
DIAMOND PORTS. 200x ,50( 8"x 2") FLOCCULATION
TIMBER BAFFLE COMPARTMENT
TYP. (HALF SHOWN)
TYPICAL SECTION
0 I 2 3 4 5 METRES
I I I [ I
n u I t 1
0 5 I0 15 20 FEET
FIGURE 6.9 Vertical paddle flocculator compartment.