Page 295 -
P. 295
10.39
OXIDATION AND DISINFECTION
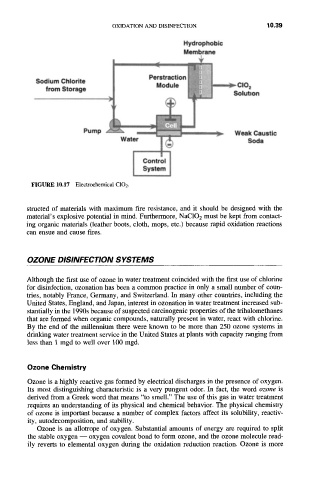
Hydrophobic
Membrane
PerstractiOnModule B
Sodium Chlorite
from Storage
Solution
Pump
Weak Caustic
Water ~ Soda
Control
System
FIGURE 10.17 Electrochemical C102.
structed of materials with maximum fire resistance, and it should be designed with the
material's explosive potential in mind. Furthermore, NaC102 must be kept from contact-
ing organic materials (leather boots, cloth, mops, etc.) because rapid oxidation reactions
can ensue and cause fires.
OZONE DISINFECTION SYSTEMS
Although the first use of ozone in water treatment coincided with the first use of chlorine
for disinfection, ozonation has been a common practice in only a small number of coun-
tries, notably France, Germany, and Switzerland. In many other countries, including the
United States, England, and Japan, interest in ozonation in water treatment increased sub-
stantially in the 1990s because of suspected carcinogenic properties of the trihalomethanes
that are formed when organic compounds, naturally present in water, react with chlorine.
By the end of the millennium there were known to be more than 250 ozone systems in
drinking water treatment service in the United States at plants with capacity ranging from
less than 1 mgd to well over 100 mgd.
Ozone Chemistry
Ozone is a highly reactive gas formed by electrical discharges in the presence of oxygen.
Its most distinguishing characteristic is a very pungent odor. In fact, the word ozone is
derived from a Greek word that means "to smell." The use of this gas in water treatment
requires an understanding of its physical and chemical behavior. The physical chemistry
of ozone is important because a number of complex factors affect its solubility, reactiv-
ity, autodecomposition, and stability.
Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen. Substantial amounts of energy are required to split
the stable oxygen -- oxygen covalent bond to form ozone, and the ozone molecule read-
ily reverts to elemental oxygen during the oxidation reduction reaction. Ozone is more