Page 105 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 105
CHAPTER 4 Hybrid Chemical EOR Using Low-Salinity and Smart Waterflood 97
100
90
80
Recovery Factor (% OOIP) 60 DB-DTAB-M-S
70
50
40
DB-DTAB-S
30
DB-DTAB
20 DB-DTAB-M
FB
10 FB-DTAB
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
Time (Days)
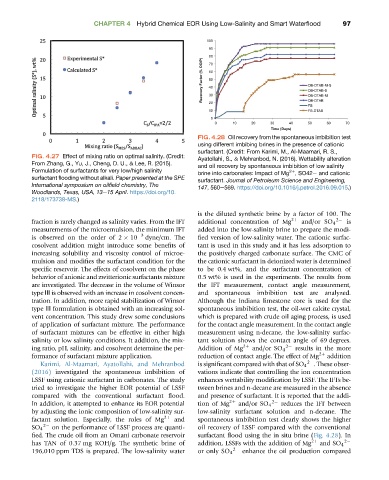
FIG. 4.28 Oil recovery from the spontaneous imbibition test
using different imbibing brines in the presence of cationic
surfactant. (Credit: From Karimi, M., Al-Maamari, R. S.,
FIG. 4.27 Effect of mixing ratio on optimal salinity. (Credit: Ayatollahi, S., & Mehranbod, N. (2016). Wettability alteration
From Zhang, G., Yu, J., Cheng, D. U., & Lee, R. (2015). and oil recovery by spontaneous imbibition of low salinity
Formulation of surfactants for very low/high salinity brine into carbonates: Impact of Mg , SO42 and cationic
2þ
surfactant flooding without alkali. Paper presented at the SPE surfactant. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,
International symposium on oilfield chemistry, The
147, 560e569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2016.09.015.)
Woodlands, Texas, USA, 13e15 April. https://doi.org/10.
2118/173738-MS.)
is the diluted synthetic brine by a factor of 100. The
fraction is rarely changed as salinity varies. From the IFT additional concentration of Mg 2þ and/or SO 4 2 is
measurements of the microemulsion, the minimum IFT added into the low-salinity brine to prepare the modi-
is observed on the order of 2 10 3 dyne/cm. The fied version of low-salinity water. The cationic surfac-
cosolvent addition might introduce some benefits of tant is used in this study and it has less adsorption to
increasing solubility and viscosity control of microe- the positively charged carbonate surface. The CMC of
mulsion and modifies the surfactant condition for the the cationic surfactant in deionized water is determined
specific reservoir. The effects of cosolvent on the phase to be 0.4 wt%, and the surfactant concentration of
behavior of anionic and zwitterionic surfactants mixture 0.5 wt% is used in the experiments. The results from
are investigated. The decrease in the volume of Winsor the IFT measurement, contact angle measurement,
type Ⅲ is observed with an increase in cosolvent concen- and spontaneous imbibition test are analyzed.
tration. In addition, more rapid stabilization of Winsor Although the Indiana limestone core is used for the
type Ⅲ formulation is obtained with an increasing sol- spontaneous imbibition test, the oil-wet calcite crystal,
vent concentration. This study drew some conclusions which is prepared with crude oil aging process, is used
of application of surfactant mixture. The performance for the contact angle measurement. In the contact angle
of surfactant mixtures can be effective in either high measurement using n-decane, the low-salinity surfac-
salinity or low salinity conditions. It addition, the mix- tant solution shows the contact angle of 69 degrees.
ing ratio, pH, salinity, and cosolvent determine the per- Addition of Mg 2þ and/or SO 4 2 results in the more
formance of surfactant mixture application. reduction of contact angle. The effect of Mg 2þ addition
Karimi, Al-Maamari, Ayatollahi, and Mehranbod is significant compared with that of SO 4 2 . These obser-
(2016) investigated the spontaneous imbibition of vations indicate that controlling the ion concentration
LSSF using cationic surfactant in carbonates. The study enhances wettability modification by LSSF. The IFTs be-
tried to investigate the higher EOR potential of LSSF tween brines and n-decane are measured in the absence
compared with the conventional surfactant flood. and presence of surfactant. It is reported that the addi-
In addition, it attempted to enhance its EOR potential tion of Mg 2þ and/or SO 4 2 reduces the IFT between
by adjusting the ionic composition of low-salinity sur- low-salinity surfactant solution and n-decane. The
factant solution. Especially, the roles of Mg 2þ and spontaneous imbibition test clearly shows the higher
2
SO 4 on the performance of LSSF process are quanti- oil recovery of LSSF compared with the conventional
fied. The crude oil from an Omani carbonate reservoir surfactant flood using the in situ brine (Fig. 4.28). In
has TAN of 0.37 mg KOH/g. The synthetic brine of addition, LSSFs with the addition of Mg 2þ and SO 4 2
196,010 ppm TDS is prepared. The low-salinity water or only SO 4 2 enhance the oil production compared