Page 145 - [B._MURPHY,_C._MURPHY,_B._HATHAWAY]_A_working_meth
P. 145
Chemical Kinetics 11 129
+
Therefore, the reaction 2C10(g) + 02(g) C12(,) is an example of a
bimolecular reaction, i.e. A + A + Products, as the two C10 gaseous
molecules collide with one another to form oxygen and chlorine gases
respectively as the products. In order for gaseous molecules to react,
they must collide with one another. The calculation of kinetic rates
from this is called The Collision Theory.
THE ACTIVATION ENERGY OF A REACTION
In Chapter 1, kinetic energy was defined as the energy a body
possesses by virtue of its motion, e.g. a moving car does work if it
collides with a wall. In the Collision Theory, a reaction is said to occur
when the two reacting molecules collide with a certain minimum
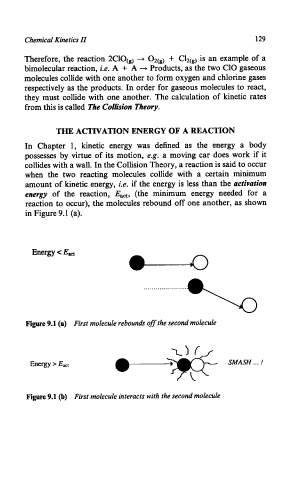
amount of kinetic energy, i.e. if the energy is less than the activation
energy of the reaction, Eact, (the minimum energy needed for a
reaction to occur), the molecules rebound off one another, as shown
in Figure 9.1 (a).
Energy < Eact
I
Figure 9.1 (a) First molecule rebounds off the second molecule
...
SMASH
.-* !
Figure 9.1 (b) First molecule interacts with the second molecule