Page 110 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 110
2.4 SPECIFIC ACQUISITION TECHNIQUES 101
to record pressure fields produced by the source recorded by horizontal (X and Y) component
arrays and perceived by suitably configured geophones/accelerometers (Fig. 2.56).
hydrophone groups. Technological develop- The primary purpose of 4C acquisition is to
ments in the last decade have allowed us to obtain a more detailed and accurate subsurface
record 4C data using different sensors directly image at the reservoir level by recording both
in contact with the sea floor. These multicompo- acoustic and elastic wave field components,
nent recording systems include three orthogo- including mode converted S waves generated
nally oriented geophones or accelerometers for by incident P waves at nonnormal incidence
3C recording as well as a hydrophone for pres- angles along the interfaces.
sure. Since S waves cannot propagate through There are three techniques which are used to
water, S wave exploration at sea can only be record ocean bottom seismic data:
achieved by 4C ocean bottom sensor recording.
While P waves are recorded by vertical compo- • Ocean bottom cable (OBC)
nent geophones/accelerometers and the hydro- • Ocean bottom seismometer (OBS)
phone, the mode converted S waves are • Ocean bottom nodes (OBN)
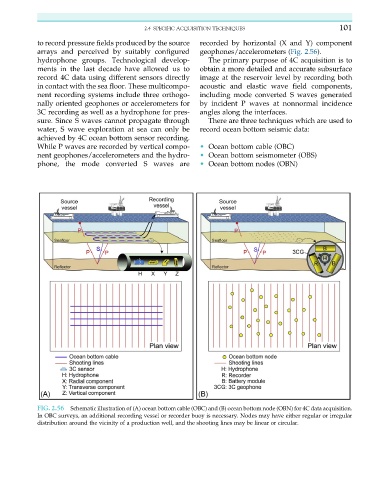
FIG. 2.56 Schematic illustration of (A) ocean bottom cable (OBC) and (B) ocean bottom node (OBN) for 4C data acquisition.
In OBC surveys, an additional recording vessel or recorder buoy is necessary. Nodes may have either regular or irregular
distribution around the vicinity of a production well, and the shooting lines may be linear or circular.