Page 105 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 105
96 2. MARINE SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION
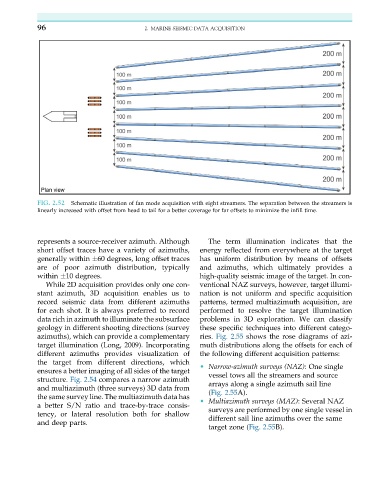
FIG. 2.52 Schematic illustration of fan mode acquisition with eight streamers. The separation between the streamers is
linearly increased with offset from head to tail for a better coverage for far offsets to minimize the infill time.
represents a source-receiver azimuth. Although The term illumination indicates that the
short offset traces have a variety of azimuths, energy reflected from everywhere at the target
generally within 60 degrees, long offset traces has uniform distribution by means of offsets
are of poor azimuth distribution, typically and azimuths, which ultimately provides a
within 10 degrees. high-quality seismic image of the target. In con-
While 2D acquisition provides only one con- ventional NAZ surveys, however, target illumi-
stant azimuth, 3D acquisition enables us to nation is not uniform and specific acquisition
record seismic data from different azimuths patterns, termed multiazimuth acquisition, are
for each shot. It is always preferred to record performed to resolve the target illumination
data rich in azimuth to illuminate the subsurface problems in 3D exploration. We can classify
geology in different shooting directions (survey these specific techniques into different catego-
azimuths), which can provide a complementary ries. Fig. 2.55 shows the rose diagrams of azi-
target illumination (Long, 2009). Incorporating muth distributions along the offsets for each of
different azimuths provides visualization of the following different acquisition patterns:
the target from different directions, which
• Narrow-azimuth surveys (NAZ): One single
ensures a better imaging of all sides of the target
vessel tows all the streamers and source
structure. Fig. 2.54 compares a narrow azimuth
arrays along a single azimuth sail line
and multiazimuth (three surveys) 3D data from
(Fig. 2.55A).
the same survey line. The multiazimuth data has
• Multiazimuth surveys (MAZ): Several NAZ
a better S/N ratio and trace-by-trace consis-
tency, or lateral resolution both for shallow surveys are performed by one single vessel in
and deep parts. different sail line azimuths over the same
target zone (Fig. 2.55B).