Page 103 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 103
94 2. MARINE SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION
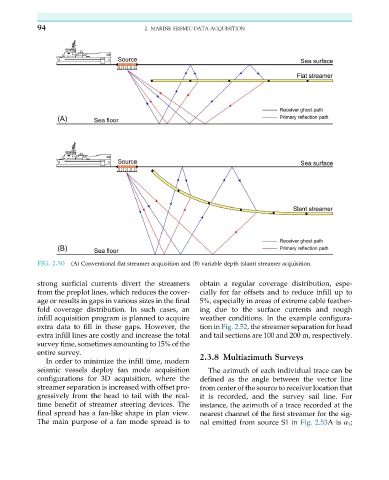
FIG. 2.50 (A) Conventional flat streamer acquisition and (B) variable depth (slant) streamer acquisition.
strong surficial currents divert the streamers obtain a regular coverage distribution, espe-
from the preplot lines, which reduces the cover- cially for far offsets and to reduce infill up to
age or results in gaps in various sizes in the final 5%, especially in areas of extreme cable feather-
fold coverage distribution. In such cases, an ing due to the surface currents and rough
infill acquisition program is planned to acquire weather conditions. In the example configura-
extra data to fill in these gaps. However, the tion in Fig. 2.52, the streamer separation for head
extra infill lines are costly and increase the total and tail sections are 100 and 200 m, respectively.
survey time, sometimes amounting to 15% of the
entire survey. 2.3.8 Multiazimuth Surveys
In order to minimize the infill time, modern
seismic vessels deploy fan mode acquisition The azimuth of each individual trace can be
configurations for 3D acquisition, where the defined as the angle between the vector line
streamer separation is increased with offset pro- from center of the source to receiver location that
gressively from the head to tail with the real- it is recorded, and the survey sail line. For
time benefit of streamer steering devices. The instance, the azimuth of a trace recorded at the
final spread has a fan-like shape in plan view. nearest channel of the first streamer for the sig-
The main purpose of a fan mode spread is to nal emitted from source S1 in Fig. 2.53Ais α 1 ;