Page 107 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 107
98 2. MARINE SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION
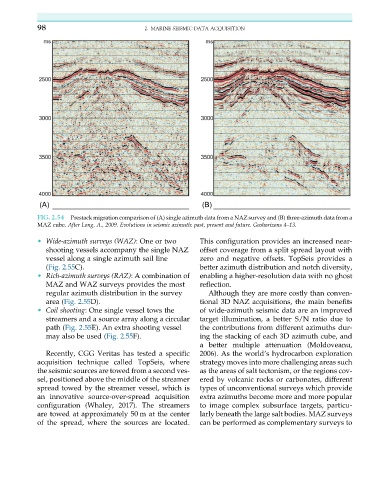
FIG. 2.54 Prestack migration comparison of (A) single azimuth data from a NAZ survey and (B) three-azimuth data from a
MAZ cube. After Long, A., 2009. Evolutions in seismic azimuth: past, present and future. Geohorizons 4–13.
• Wide-azimuth surveys (WAZ): One or two This configuration provides an increased near-
shooting vessels accompany the single NAZ offset coverage from a split spread layout with
vessel along a single azimuth sail line zero and negative offsets. TopSeis provides a
(Fig. 2.55C). better azimuth distribution and notch diversity,
• Rich-azimuth surveys (RAZ): A combination of enabling a higher-resolution data with no ghost
MAZ and WAZ surveys provides the most reflection.
regular azimuth distribution in the survey Although they are more costly than conven-
area (Fig. 2.55D). tional 3D NAZ acquisitions, the main benefits
• Coil shooting: One single vessel tows the of wide-azimuth seismic data are an improved
streamers and a source array along a circular target illumination, a better S/N ratio due to
path (Fig. 2.55E). An extra shooting vessel the contributions from different azimuths dur-
may also be used (Fig. 2.55F). ing the stacking of each 3D azimuth cube, and
a better multiple attenuation (Moldoveanu,
Recently, CGG Veritas has tested a specific 2006). As the world’s hydrocarbon exploration
acquisition technique called TopSeis, where strategy moves into more challenging areas such
the seismic sources are towed from a second ves- as the areas of salt tectonism, or the regions cov-
sel, positioned above the middle of the streamer ered by volcanic rocks or carbonates, different
spread towed by the streamer vessel, which is types of unconventional surveys which provide
an innovative source-over-spread acquisition extra azimuths become more and more popular
configuration (Whaley, 2017). The streamers to image complex subsurface targets, particu-
are towed at approximately 50 m at the center larly beneath the large salt bodies. MAZ surveys
of the spread, where the sources are located. can be performed as complementary surveys to