Page 141 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 141
132 2. MARINE SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION
ensure that the quality, accuracy and resolution • Sum of all channels of each streamer per shot
of the acquired data meet the predetermined (electrical noise and cross feed)
requirements and are within the specified limits. • RMS noise display of all channels (ambient
QC procedures enable us to identify any issues and operational noise level)
during the acquisition as soon as they occur, • Mean amplitude spectra
which may result in reshooting some of the lines • Depth display of the streamers
or a temporary suspension of the whole survey. • Gun depth for each subarray
Identifying acquisition problems arising from • Gun pressure for each subarray
the instruments or weather conditions as well • Real-time fold distribution
as software specifications such as bad records, • Checking the data header values
misfires, defective or dead channels, air leakages, • Separation and feathering of the streamers
specific strong noise interferences, etc., early in
After a seismic line is acquired and recorded,
the data collection minimizes the technical down-
offline QC processing is initiated. Each member
times during the acquisition.
of the survey crew in Fig. 2.1 has different
QC in data acquisition is fulfilled as real-time
responsibilities in terms of QC applications just
(or online) and offline implementations
before, during and after the data acquisition. A
(Fig. 2.82). Online QC involves analyzing the
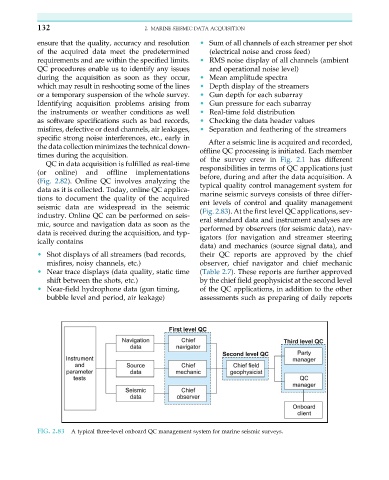
typical quality control management system for
data as it is collected. Today, online QC applica-
marine seismic surveys consists of three differ-
tions to document the quality of the acquired
ent levels of control and quality management
seismic data are widespread in the seismic
(Fig. 2.83). At the first level QC applications, sev-
industry. Online QC can be performed on seis-
eral standard data and instrument analyses are
mic, source and navigation data as soon as the
performed by observers (for seismic data), nav-
data is received during the acquisition, and typ-
ically contains igators (for navigation and streamer steering
data) and mechanics (source signal data), and
• Shot displays of all streamers (bad records, their QC reports are approved by the chief
misfires, noisy channels, etc.) observer, chief navigator and chief mechanic
• Near trace displays (data quality, static time (Table 2.7). These reports are further approved
shift between the shots, etc.) by the chief field geophysicist at the second level
• Near-field hydrophone data (gun timing, of the QC applications, in addition to the other
bubble level and period, air leakage) assessments such as preparing of daily reports
FIG. 2.83 A typical three-level onboard QC management system for marine seismic surveys.