Page 509 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 509
500 11. SEISMIC MIGRATION
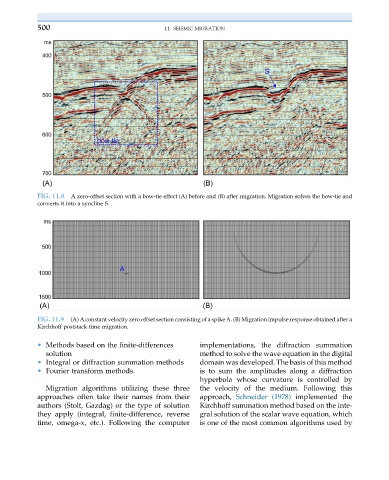
FIG. 11.8 A zero-offset section with a bow-tie effect (A) before and (B) after migration. Migration solves the bow-tie and
converts it into a syncline S.
FIG. 11.9 (A) A constant velocity zero offset section consisting of a spike A. (B) Migration impulse response obtained after a
Kirchhoff poststack time migration.
• Methods based on the finite-differences implementations, the diffraction summation
solution method to solve the wave equation in the digital
• Integral or diffraction summation methods domain was developed. The basis of this method
• Fourier transform methods. is to sum the amplitudes along a diffraction
hyperbola whose curvature is controlled by
Migration algorithms utilizing these three the velocity of the medium. Following this
approaches often take their names from their approach, Schneider (1978) implemented the
authors (Stolt, Gazdag) or the type of solution Kirchhoff summation method based on the inte-
they apply (integral, finite-difference, reverse gral solution of the scalar wave equation, which
time, omega-x, etc.). Following the computer is one of the most common algorithms used by