Page 193 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 193
178 ZEOLITES AND MOLECULAR SIEVES
Table 7.4. Cation site occupancies in dehydrated X and Y zeolites
Zeolite Al/Unit Sites
Cell
I I’ II II’ III
Li-X (Li-LSX) a 95.8 — 27.2 33.9 — 32.4
Li-X b 85 — 25.6 30.4 — 11.5
Li-Y c 46 — 24.4 21.0 — 0
Na-X d 81 3.8 32.3 30.8 — 7.9
Na-Y e 53 3 15 35 — —
Na-Y f 57 7.8 20.2 31.2 — —
K-Y g 54.7 5.4 18.1 26.8 — —
K-X h 87 9 13 26 — 38
Ca-X g 86 7.5 17.3 17.3 9.0 —
Sr-X g 86 11.2 7.0 19.5 4.2 —
Ba 36 Na 16 -X i 88 7.0 Ba 4.7 Ba 11.4 Ba 3.7Ba Na
Ag-LSX j 96 8.5 23.4 32.0 0 19.2
Ag-Y j 56 10.9 12.4 27.5 4.5 0
a Hutson and Yang, 2000.
b Feuerstein and Lobo, 1998.
c Forano et al., 1989.
d Mortier, 1982.
e Engelhardt et al., 1994.
f Eulenberger et al., 1967a.
g Mortier et al., 1972.
h
Hseu, 1972.
i
Olson, 1968.
j
Hutson et al., 2000.
Maximum = 96 monovalent cations per unit cell for Si/Al = 1.
III
I
IV
II
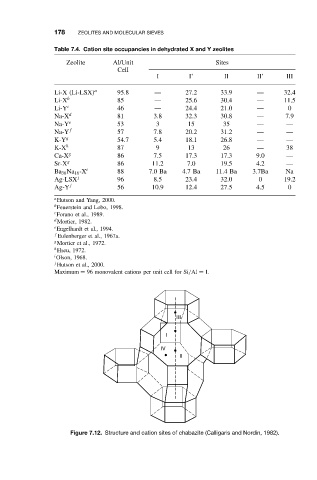
Figure 7.12. Structure and cation sites of chabazite (Calligaris and Nordin, 1982).