Page 197 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 197
182 ZEOLITES AND MOLECULAR SIEVES
25
N adsorption at 25°C
2
(a)
J J
J
20 J J (b)
J H H
J H H H H B (c) B
Amount adsorbed (molec/uc) 10 J J H J B H B B B B BB H F B F B F F (d) F
J
HH H H H H H H
J
15
B
B
F
5
F B J B F
0 F
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Pressure (atm)
◦
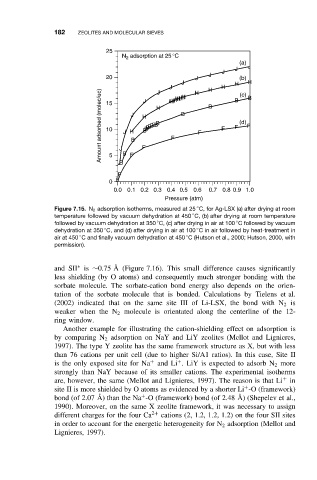
Figure 7.15. N 2 adsorption isotherms, measured at 25 C, for Ag-LSX (a) after drying at room
◦
temperature followed by vacuum dehydration at 450 C, (b) after drying at room temperature
◦
◦
followed by vacuum dehydration at 350 C, (c) after drying in air at 100 C followed by vacuum
◦
◦
dehydration at 350 C, and (d) after drying in air at 100 C in air followed by heat-treatment in
◦
◦
air at 450 C and finally vacuum dehydration at 450 C (Hutson et al., 2000; Hutson, 2000, with
permission).
∗
and SII is ∼0.75 ˚ A (Figure 7.16). This small difference causes significantly
less shielding (by O atoms) and consequently much stronger bonding with the
sorbate molecule. The sorbate-cation bond energy also depends on the orien-
tation of the sorbate molecule that is bonded. Calculations by Tielens et al.
(2002) indicated that on the same site III of Li-LSX, the bond with N 2 is
weaker when the N 2 molecule is orientated along the centerline of the 12-
ring window.
Another example for illustrating the cation-shielding effect on adsorption is
by comparing N 2 adsorption on NaY and LiY zeolites (Mellot and Lignieres,
1997). The type Y zeolite has the same framework structure as X, but with less
than 76 cations per unit cell (due to higher Si/A1 ratios). In this case, Site II
+
is the only exposed site for Na and Li . LiY is expected to adsorb N 2 more
+
strongly than NaY because of its smaller cations. The experimental isotherms
+
are, however, the same (Mellot and Lignieres, 1997). The reason is that Li in
+
site II is more shielded by O atoms as evidenced by a shorter Li -O (framework)
+
bond (of 2.07 ˚ A) than the Na -O (framework) bond (of 2.48 ˚ A) (Shepelev et al.,
1990). Moreover, on the same X zeolite framework, it was necessary to assign
different charges for the four Ca 2+ cations (2, 1.2, 1.2, 1.2) on the four SII sites
in order to account for the energetic heterogeneity for N 2 adsorption (Mellot and
Lignieres, 1997).