Page 199 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 199
184 ZEOLITES AND MOLECULAR SIEVES
12
11
10 J J
Heat of adsorption (kcal/mol) 8 J J J J J J J J J J (a) J
9
7
6
5
4 BBB B B B B B B B B B B (b)
3
2
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Coverage (molec/uc)
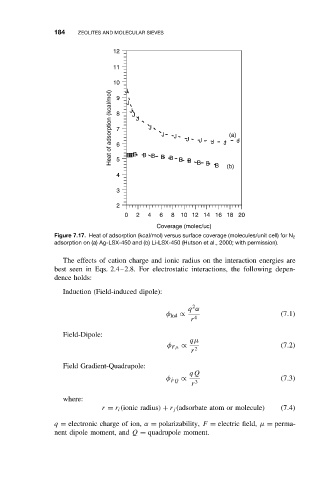
Figure 7.17. Heat of adsorption (kcal/mol) versus surface coverage (molecules/unit cell) for N 2
adsorption on (a) Ag-LSX-450 and (b) Li-LSX-450 (Hutson et al., 2000; with permission).
The effects of cation charge and ionic radius on the interaction energies are
best seen in Eqs. 2.4–2.8. For electrostatic interactions, the following depen-
dence holds:
Induction (Field-induced dipole):
2
q α
φ Ind ∝ (7.1)
r 4
Field-Dipole:
qµ
φ Fµ ∝ (7.2)
r 2
Field Gradient-Quadrupole:
qQ
∝ (7.3)
φ ˙ FQ
r 3
where:
r = r i (ionic radius) + r j (adsorbate atom or molecule) (7.4)
q = electronic charge of ion, α = polarizability, F = electric field, µ = perma-
nent dipole moment, and Q = quadrupole moment.