Page 240 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 240
PURIFICATION BY π-COMPLEXATION 225
60
1,3-butadiene on Ag-Y(2.43) 1,3-butadiene on Ag-Y(6)
1,3-butadiene on Ag-Y(15) 1,3-butadiene on Ag-Y(195)
1-butene on Ag-Y(2.43) 1-butene on Ag-Y(6) Ag-Y(15)
Amount adsorbed (molecules/u.c.) 40 Ag-Y(2.43) Ag-Y(6) Ag-Y(2.43)
50
1-butene on Ag-Y(195)
1-butene on Ag-Y(15)
30
20
Ag-Y(6)
Ag-Y(15)
10
Ag-Y(195)
0
1.E−05 1.E−04 1.E−03 1.E−02 1.E−01 1.E+00
Partial pressure (atm)
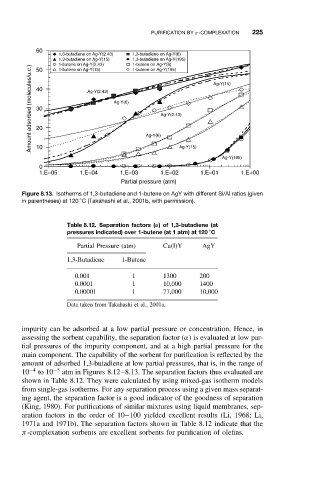
Figure 8.13. Isotherms of 1,3-butadiene and 1-butene on AgY with different Si/Al ratios (given
◦
in parentheses) at 120 C (Takahashi et al., 2001b, with permission).
Table 8.12. Separation factors (α) of 1,3-butadiene (at
◦
pressures indicated) over 1-butene (at 1 atm) at 120 C
Partial Pressure (atm) Cu(I)Y AgY
1,3-Butadiene 1-Butene
0.001 1 1300 200
0.0001 1 10,000 1400
0.00001 1 77,000 10,000
Data taken from Takahashi et al., 2001a.
impurity can be adsorbed at a low partial pressure or concentration. Hence, in
assessing the sorbent capability, the separation factor (α) is evaluated at low par-
tial pressures of the impurity component, and at a high partial pressure for the
main component. The capability of the sorbent for purification is reflected by the
amount of adsorbed 1,3-butadiene at low partial pressures, that is, in the range of
10 −4 to 10 −5 atm in Figures 8.12–8.13. The separation factors thus evaluated are
shown in Table 8.12. They were calculated by using mixed-gas isotherm models
from single-gas isotherms. For any separation process using a given mass separat-
ing agent, the separation factor is a good indicator of the goodness of separation
(King, 1980). For purifications of similar mixtures using liquid membranes, sep-
aration factors in the order of 10–100 yielded excellent results (Li, 1968; Li,
1971a and 1971b). The separation factors shown in Table 8.12 indicate that the
π-complexation sorbents are excellent sorbents for purification of olefins.