Page 256 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 256
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH004.qxd 7/1/2006 6:53 PM Page 252
252 4. Adsorption and Ion Exchange
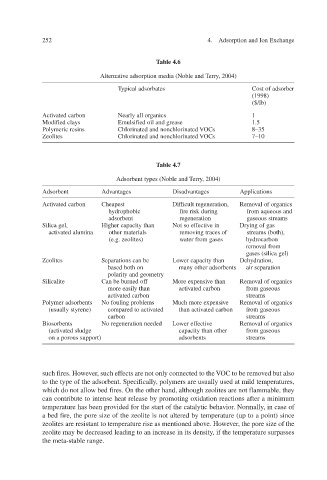
Table 4.6
Alternative adsorption media (Noble and Terry, 2004)
Typical adsorbates Cost of adsorber
(1998)
($/lb)
Activated carbon Nearly all or ganics 1
Modified clays Emulsified oil and grease 1.5
Polymeric resins Chlorinated and nonchlorinated OCs V 8–35
Zeolites Chlorinated and nonchlorinated OCs V 7–10
Table 4.7
erry, Adsorbent types (Noble and T2004)
Adsorbent Advantages Disadvantages Applications
Activated carbon Cheapest Difficult regeneration, Removal of organics
hydrophobic fire risk during from aqueous and
adsorbent regeneration gaseous streams
Silica gel, Higher capacity than Not so efve in fecti Drying of gas
activated alumina other materials removing traces of streams (both),
(e.g. zeolites) water from gases hydrocarbon
removal from
gases (silica gel)
Zeolites Separations can be Lower capacity than Dehydration,
based both on many other adsorbents air separation
polarity and geometry
Silicalite f Can be burned of xpensi More eve than Removal of organics
more easily than activated carbon from gaseous
activated carbon streams
Polymer adsorbents No fouling problems xpensi v Much more ee Removal of organics
(usually styrene) compared to actiated v than activated carbon from gaseous
carbon streams
Biosorbents No regeneration needed Lower effective Removal of organics
(activated sludge capacity than other from gaseous
on a porous support) adsorbents streams
such fires. However, such effects are not only connected to the VOC to be removed but also
to the type of the adsorbent. Specif polymers are usually used at mild temperatures, , ically
which do not allow bed fires. On the other hand, although zeolites are not flammable, the y
can contribute to intense heat release by promoting oxidation reactions after a minimum
temperature has been provided for the start of the catalytic beha in case of , . Normally vior
ire,
a bed f the pore size of the zeolite is not altered by temperature (up to a point) since
zeolites are resistant to temperature rise as mentioned above. However, the pore size of the
, zeolite may be decreased leading to an increase in its density if the temperature surpasses
the meta-stable range.