Page 1057 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1057
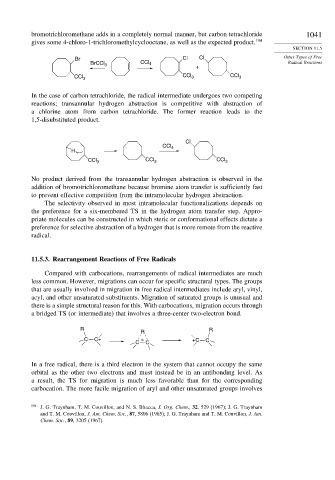
bromotrichloromethane adds in a completely normal manner, but carbon tetrachloride 1041
gives some 4-chloro-1-trichloromethylcyclooctane, as well as the expected product. 194
SECTION 11.5
Br Cl Cl Other Types of Free
BrCCl 3 CCl 4 Radical Reactions
+
CCl CCl
CCl 3 3 3
In the case of carbon tetrachloride, the radical intermediate undergoes two competing
reactions; transannular hydrogen abstraction is competitive with abstraction of
a chlorine atom from carbon tetrachloride. The former reaction leads to the
1,5-disubstituted product.
Cl
. . CCl 4
H
CCl 3 CCl 3 CCl 3
No product derived from the transannular hydrogen abstraction is observed in the
addition of bromotrichloromethane because bromine atom transfer is sufficiently fast
to prevent effective competition from the intramolecular hydrogen abstraction.
The selectivity observed in most intramolecular functionalizations depends on
the preference for a six-membered TS in the hydrogen atom transfer step. Appro-
priate molecules can be constructed in which steric or conformational effects dictate a
preference for selective abstraction of a hydrogen that is more remote from the reactive
radical.
11.5.3. Rearrangement Reactions of Free Radicals
Compared with carbocations, rearrangements of radical intermediates are much
less common. However, migrations can occur for specific structural types. The groups
that are usually involved in migration in free radical intermediates include aryl, vinyl,
acyl, and other unsaturated substituents. Migration of saturated groups is unusual and
there is a simple structural reason for this. With carbocations, migration occurs through
a bridged TS (or intermediate) that involves a three-center two-electron bond.
R R
R
C C+ + +C C
C C
In a free radical, there is a third electron in the system that cannot occupy the same
orbital as the other two electrons and must instead be in an antibonding level. As
a result, the TS for migration is much less favorable than for the corresponding
carbocation. The more facile migration of aryl and other unsaturated groups involves
194
J. G. Traynham, T. M. Couvillon, and N. S. Bhacca, J. Org. Chem., 32, 529 (1967); J. G. Traynham
and T. M. Couvillon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 87, 5806 (1965); J. G. Traynham and T. M. Couvillon, J. Am.
Chem. Soc., 89, 3205 (1967).