Page 169 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 169
The conformational profile for 2-butanone has been developed from analysis of its 149
infrared spectrum. 35 The dominant conformation is anti with a C(1)H and the C(4)
methyl group eclipsed with the carbonyl. SECTION 2.2
Conformation
H
H O
H
H
H
H H H
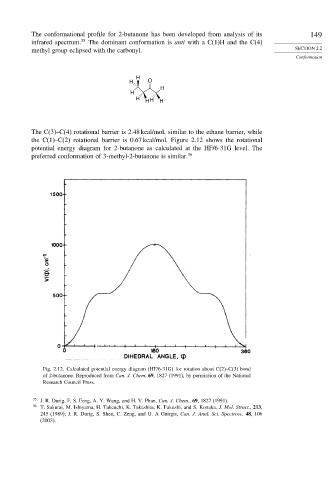
The C(3)–C(4) rotational barrier is 2.48 kcal/mol, similar to the ethane barrier, while
the C(1)–C(2) rotational barrier is 0.67 kcal/mol. Figure 2.12 shows the rotational
potential energy diagram for 2-butanone as calculated at the HF/6-31G level. The
preferred conformation of 3-methyl-2-butanone is similar. 36
Fig. 2.12. Calculated potential energy diagram (HF/6-31G) for rotation about C(2)–C(3) bond
of 2-butanone. Reproduced from Can. J. Chem. 69, 1827 (1991), by permission of the National
Research Council Press.
35 J. R. Durig, F. S. Feng, A. Y. Wang, and H. V. Phan, Can. J. Chem., 69, 1827 (1991).
36
T. Sakurai, M. Ishiyama, H. Takeuchi, K. Takeshita, K. Fukushi, and S. Konaka, J. Mol. Struct., 213,
245 (1989); J. R. Durig, S. Shen, C. Zeng, and G. A Guirgis, Can. J. Anal. Sci. Spectrosc. 48, 106
(2003).