Page 402 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 402
reactivity. The changes in chemical shifts of C(4) in some substituted benzenes 383
are given below. Plot these against , , and . What conclusions do you
+
−
PROBLEMS
draw from these plots in regard to the mix of resonance and polar components
in each of the values?
X a X a
−9 86 3 29
NH 2 CF 3
CH 3 O −7 75 CN 3 80
F −4 49 CH 3 CO 4 18
Cl −2 05 CH 3 O 2 C 4 12
Br −1 62 CH 3 SO 2 4 64
−2 89 5 53
CH 3 NO 2
a. is the change in chemical shift in ppm relative to benzene
in CCl 4 solution.
3.15. The ionization constants pK of 4-substituted pyridines have been measured,
a
as have the H of ionization at 25 C. Calculate S for each ionization. Compare
the contribution of H and S to the free energy of ionization. Test the data
for linear free-energy correlations. Are the LFER dominated by the H or S
term?
X N + H X N + H +
X pK a H (kcal/mol) X pK a H (kcal/mol)
H 5 21 4 8 Cl 3 83 3 6
9 12 11 3 Br 3 75 3 5
NH 2
CH 3 O 6 58 6 8 CN 1 86 1 3
6 03 6 1
CH 3
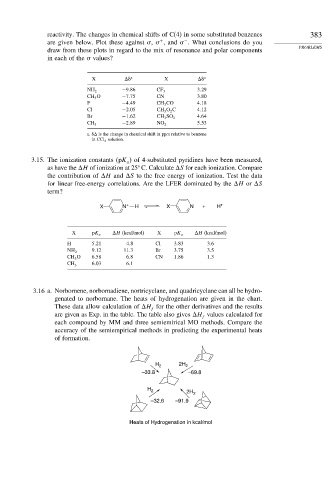
3.16 a. Norbornene, norbornadiene, nortricyclane, and quadricyclane can all be hydro-
genated to norbornane. The heats of hydrogenation are given in the chart.
These data allow calculation of H for the other derivatives and the results
f
are given as Exp. in the table. The table also gives H values calculated for
f
each compound by MM and three semiemirical MO methods. Compare the
accuracy of the semiempirical methods in predicting the experimental heats
of formation.
H 2 2H 2
–33.8 –69.8
H 2 2H 2
–32.6 –91.9
Heats of Hydrogenation in kcal/mol