Page 406 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 406
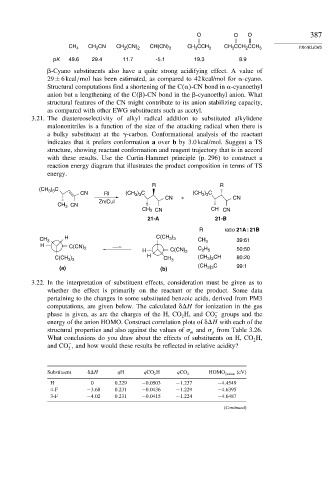
O O O 387
CH CN CH (CN) CH CCH CCH
CH 4 3 2 2 CH(CN) 3 CH 3 CCH 3 3 2 3 PROBLEMS
pK 49.6 29.4 11.7 -5.1 19.3 8.9
-Cyano substituents also have a quite strong acidifying effect. A value of
29 ± 6kcal/mol has been estimated, as compared to 42 kcal/mol for -cyano.
Structural computations find a shortening of the C -CN bond in -cyanoethyl
anion but a lengthening of the C -CN bond in the -cyanoethyl anion. What
structural features of the CN might contribute to its anion stabilizing capacity,
as compared with other EWG substituents such as acetyl.
3.21. The diastereoselectivity of alkyl radical addition to substituted alkylidene
malononitriles is a function of the size of the attacking radical when there is
a bulky substituent at the -carbon. Conformational analysis of the reactant
indicates that it prefers conformation a over b by 3.0 kcal/mol. Suggest a TS
structure, showing reactant conformation and reagent trajectory that is in accord
with these results. Use the Curtin-Hammet principle (p. 296) to construct a
reaction energy diagram that illustrates the product composition in terms of TS
energy.
R R
(CH ) C
3 3
CN RI (CH ) C (CH ) C
3 3
3 3
CN + CN
Zn/CuI
CH 3 CN
CH 3 CN CH CN
21-A 21-B
R ratio 21A : 21B
3 3
CH 3 H C(CH ) CH 3 39:61
H
C(CN) 2 C H 50:50
H C(CN) 2 2 5
C(CH ) H CH 3 (CH ) CH 80:20
3 2
3 3
(CH C 99:1
(a) (b) 3)3
3.22. In the interpretation of substituent effects, consideration must be given as to
whether the effect is primarily on the reactant or the product. Some data
pertaining to the changes in some substituted benzoic acids, derived from PM3
computations, are given below. The calculated H for ionization in the gas
−
phase is given, as are the charges of the H, CO H, and CO groups and the
2 2
energy of the anion HOMO. Construct correlation plots of H with each of the
structural properties and also against the values of and from Table 3.26.
m
p
What conclusions do you draw about the effects of substituents on H, CO H,
2
−
and CO , and how would these results be reflected in relative acidity?
2
Substituent H qH qCO 2 H qCO 2 − HOMO anion (eV)
H 0 0 229 −0 0503 −1 237 −4 4549
4-F −3 68 0 231 −0 0436 −1 229 −4 6395
3-F −4 02 0 231 −0 0415 −1 224 −4 6487
(Continued)