Page 404 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 404
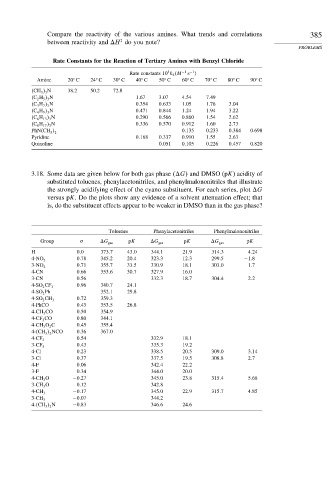
Compare the reactivity of the various amines. What trends and correlations 385
‡
between reactivity and H do you note?
PROBLEMS
Rate Constants for the Reaction of Tertiary Amines with Benzyl Chloride
5
Rate constants 10 k 2 M −1 −1
s
Amine 20 C 24 C 30 C 40 C 50 C 60 C 70 C 80 C 90 C
CH 3 3 N 38.2 50.2 72.8
C 2 H 5 3 N 1 67 3 07 4 54 7 49
C 3 H 7 3 N 0 354 0 633 1 05 1 76 3 04
C 4 H 9 3 N 0 471 0 844 1 24 1 94 3 22
C 6 H 13 3 N 0 290 0 566 0 860 1 54 2 62
C 8 H 17 3 N 0 336 0 570 0 912 1 60 2 73
0 135 0 233 0 384 0.698
PhN CH 3 2
Pyridine 0 168 0 337 0 910 1 55 2 63
Quinoline 0 051 0 105 0 226 0 457 0.820
3.18. Some data are given below for both gas phase G and DMSO (pK) acidity of
substituted toluenes, phenylacetonitriles, and phenylmalononitriles that illustrate
the strongly acidifying effect of the cyano substituent. For each series, plot G
versus pK. Do the plots show any evidence of a solvent attenuation effect; that
is, do the substituent effects appear to be weaker in DMSO than in the gas phase?
Toluenes Phenylacetonitriles Phenylmalononitriles
Group G gas pK G gas pK G gas pK
H 0 0 373 7 43 0 344 1 21 9 314 3 4 24
0 78 345 2 20 4 323 3 12 3 299 5 −1 8
4-NO 2
0 71 355 7 33 5 330 9 18 1 303 0 1 7
3-NO 2
4-CN 0 66 353 6 30 7 327 9 16 0
3-CN 0 56 332 3 18 7 304 4 2 2
0 96 340 7 24 1
4-SO 2 CF 3
4-SO 2 Ph 352 1 29 8
0 72 359 3
4-SO 2 CH 3
4-PhCO 0 43 353 5 26 8
4-CH 3 CO 0 50 354 9
4-CF 3 CO 0 80 344 1
4-CH 3 O 2 C 0 45 355 4
4- CH 3 2 NCO 0 36 367 0
0 54 332 9 18 1
4-CF 3
0 43 335 3 19 2
3-CF 3
4-Cl 0 23 338 5 20 5 309 0 3 14
3-Cl 0 37 337 5 19 5 308 8 2 7
4-F 0 06 342 4 22 2
3-F 0 34 344 0 20 0
4-CH 3 O −0 27 345 0 23 8 315 4 5 68
3-CH 3 O 0 12 342 8
−0 17 345 0 22 9 315 7 4 85
4-CH 3
−0 07 344 2
3-CH 3
4- CH 3 2 N −0 83 346 6 24 6