Page 403 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 403
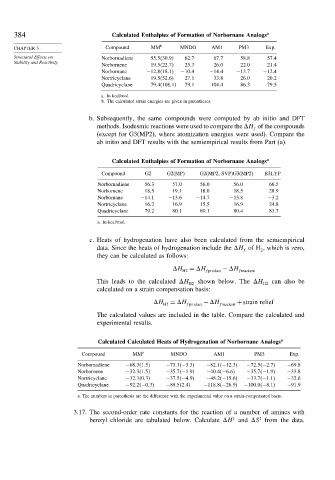
384 Calculated Enthalpies of Formation of Norbornane Analogs a
CHAPTER 3 Compound MM b MNDO AM1 PM3 Exp.
Structural Effects on Norbornadiene 55 5 30 9 62 7 67 7 58 8 57 4
Stability and Reactivity
Norbornene 19 5 22 7 25 3 26 0 22 0 21 4
Norbornane −12 8 18 1 −10 4 −14 4 −13 7 −12 4
Nortricyclane 19 5 52 6 27 1 33 8 26 0 20 2
Quadricyclane 79 4 108 1 79 1 104 4 86 3 79 5
a. In kcal/mol.
b. The calculated strain energies are given in parentheses.
b. Subsequently, the same compounds were computed by ab initio and DFT
methods. Isodesmic reactions were used to compare the H of the compounds
f
(except for G3(MP2), where atomization energies were used). Compare the
ab initio and DFT results with the semiempirical results from Part (a).
Calculated Enthalpies of Formation of Norbornane Analogs a
Compound G2 G2(MP) G2(MP2, SVP)G3(MP2) B3LYP
Norbornadiene 56 3 57 0 56 0 56 0 66 5
Norbornene 18 5 19 1 18 0 18 5 28 9
Norbornane −14 1 −13 6 −14 7 −13 8 −3 2
Nortricyclane 16 2 16 9 15 5 16 9 24 8
Quadricyclane 79 2 80 1 80 1 80 4 83 7
a. In kcal/mol.
c. Heats of hydrogenation have also been calculated from the semiempirical
data. Since the heats of hydrogenation include the H of H , which is zero,
f
2
they can be calculated as follows:
H H2 = H fproduct − H freactant
This leads to the calculated H H2 shown below. The H H2 can also be
calculated on a strain compensation basis:
H H2 = H fproduct − H freactant +strain relief
The calculated values are included in the table. Compare the calculated and
experimental results.
Calculated Calculated Heats of Hydrogenation of Norbornane Analogs a
Compound MM b MNDO AM1 PM3 Exp.
Norbornadiene −68 3 1 5 −73 1 −3 3 −82 1 −12 3 −72 5 −2 7 −69 8
Norbornene −32 3 1 5 −35 7 −1 9 −40 4 −6 6 −35 7 −1 9 −33 8
Nortricyclane −32 3 0 3 −37 5 −4 9 −48 2 −15 6 −33 7 −1 1 −32 6
Quadricyclane −92 2 −0 3 −89 5 2 4 −118 8 −26 9 −100 0 −8 1 −91 9
a. The numbers in parenthesis are the difference with the experimental value on a strain-compensated basis.
3.17. The second-order rate constants for the reaction of a number of amines with
‡
‡
benzyl chloride are tabulated below. Calculate H and S from the data.