Page 405 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 405
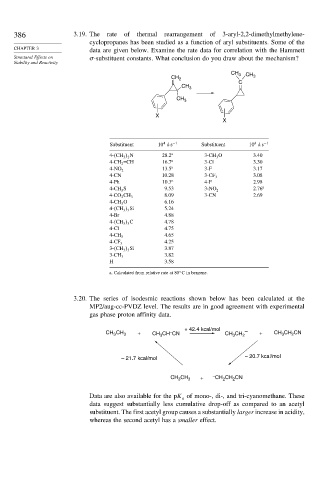
386 3.19. The rate of thermal rearrangement of 3-aryl-2,2-dimethylmethylene-
cyclopropanes has been studied as a function of aryl substituents. Some of the
CHAPTER 3 data are given below. Examine the rate data for correlation with the Hammett
Structural Effects on -substituent constants. What conclusion do you draw about the mechanism?
Stability and Reactivity
CH 3 CH
CH 2 3
C
CH 3
CH 3
X
X
4
4
Substituent 10 ks −1 Substituent 10 ks −1
4- CH 3 2 N 28.2 a 3-CH 3 O 3.40
4-CH 2 =CH 16.7 a 3-Cl 3.30
13.5 a 3-F 3.17
4-NO 2
4-CN 10.28 3-CF 3 3.08
4-Ph 10.3 a 4-F 2.98
4-CH 3 S 9.53 3-NO 2 2.76 a
8.09 3-CN 2.69
4-CO 2 CH 3
4-CH 3 O 6.16
4- CH 3 3 Si 5.24
4-Br 4.88
4- CH 3 3 C 4.78
4-Cl 4.75
4.65
4-CH 3
4.25
4-CF 3
3- CH 3 3 Si 3.87
3.82
3-CH 3
H 3.58
a. Calculated from relative rate at 80 C in benzene.
3.20. The series of isodesmic reactions shown below has been calculated at the
MP2/aug-cc-PVDZ level. The results are in good agreement with experimental
gas phase proton affinity data.
+ 42.4 kcal/mol
CH CH 3 + CH CH CN CH CH 2 – + CH 3 CH CN
–
3
2
3
3
– 21.7 kcal/mol – 20.7 kcal/mol
CH CH 3 + – CH CH CN
2
2
3
Data are also available for the pK of mono-, di-, and tri-cyanomethane. These
a
data suggest substantially less cumulative drop-off as compared to an acetyl
substituent. The first acetyl group causes a substantially larger increase in acidity,
whereas the second acetyl has a smaller effect.