Page 42 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 42
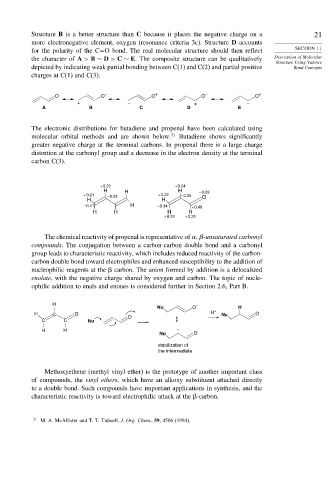
Structure B is a better structure than C because it places the negative charge on a 21
more electronegative element, oxygen (resonance criteria 3c). Structure D accounts
for the polarity of the C=O bond. The real molecular structure should then reflect SECTION 1.1
the character of A > B ∼ D > C ∼ E. The composite structure can be qualitatively Description of Molecular
Structure Using Valence
depicted by indicating weak partial bonding between C(1) and C(2) and partial positive Bond Concepts
charges at C(1) and C(3).
– + – +
O O O O O
+ – + –
A B C D E
The electronic distributions for butadiene and propenal have been calculated using
molecular orbital methods and are shown below. 31 Butadiene shows significantly
greater negative charge at the terminal carbons. In propenal there is a large charge
distortion at the carbonyl group and a decrease in the electron density at the terminal
carbon C(3).
+ 0.22 + 0.24
H H H – 0.69
+ 0.21 – 0.23 + 0.22 – 0.35 O
H H
– 0.41 H – 0.34 + 0.48
H H H H
+ 0.22 + 0.22
The chemical reactivity of propenal is representative of
-unsaturated carbonyl
compounds. The conjugation between a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbonyl
group leads to characteristic reactivity, which includes reduced reactivity of the carbon-
carbon double bond toward electrophiles and enhanced susceptibility to the addition of
nucleophilic reagents at the carbon. The anion formed by addition is a delocalized
enolate, with the negative charge shared by oxygen and carbon. The topic of nucle-
ophilic addition to enals and enones is considered further in Section 2.6, Part B.
H
Nu O – H
H C O O H + Nu O
C C Nu
H H –
Nu O
stabilization of
the intermediate
Methoxyethene (methyl vinyl ether) is the prototype of another important class
of compounds, the vinyl ethers, which have an alkoxy substituent attached directly
to a double bond. Such compounds have important applications in synthesis, and the
characteristic reactivity is toward electrophilic attack at the -carbon.
31
M. A. McAllister and T. T. Tidwell, J. Org. Chem., 59, 4506 (1994).