Page 462 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 462
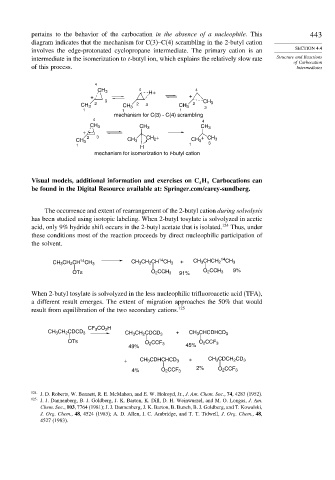
pertains to the behavior of the carbocation in the absence of a nucleophile. This 443
diagram indicates that the mechanism for C(3)–C(4) scrambling in the 2-butyl cation
involves the edge-protonated cyclopropane intermediate. The primary cation is an SECTION 4.4
intermediate in the isomerization to t-butyl ion, which explains the relatively slow rate Structure and Reactions
of Carbocation
of this process. Intermediates
4
4 4
CH 3
H+
+ +
3
2 2 2 CH 3
CH 3 CH 3 3 CH 3 3
1 1 1
mechanism for C(3) - C(4) scrambling
4
4
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
+
2 3 CH 2 + + CH 3
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 3
1 1
H
mechanism for isomerization to t-butyl cation
Visual models, additional information and exercises on C H Carbocations can
9
4
be found in the Digital Resource available at: Springer.com/carey-sundberg.
The occurrence and extent of rearrangement of the 2-butyl cation during solvolysis
has been studied using isotopic labeling. When 2-butyl tosylate is solvolyzed in acetic
acid, only 9% hydride shift occurs in the 2-butyl acetate that is isolated. 124 Thus, under
these conditions most of the reaction proceeds by direct nucleophilic participation of
the solvent.
14 14 + 14
CH 3 CH 2 CH CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 CH CH 3 CH 3 CHCH 2 CH 3
OTs O 2 CCH 3 91% O 2 CCH 3 9%
When 2-butyl tosylate is solvolyzed in the less nucleophilic trifluoroacetic acid (TFA),
a different result emerges. The extent of migration approaches the 50% that would
result from equilibration of the two secondary cations. 125
CF 3 CO 2 H
CH 3 CH 2 CDCD 3 + CH 3 CHCDHCD 3
CH 3 CH 2 CDCD 3
OTs O 2 CCF 3 O 2 CCF 3
49% 45%
+ CH 3 CDHCHCD 3 + CH 3 CDCH 2 CD 3
4% O 2 CCF 3 2% O 2 CCF 3
124 J. D. Roberts, W. Bennett, R. E. McMahon, and E. W. Holroyd, Jr., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 74, 4283 (1952).
125
J. J. Dannenberg, B. J. Goldberg, J. K. Barton, K. Dill, D. H. Weinwurzel, and M. O. Longas, J. Am.
Chem. Soc., 103, 7764 (1981); J. J. Dannenberg, J. K. Barton, B. Bunch, B. J. Goldberg, and T. Kowalski,
J. Org. Chem., 48, 4524 (1983); A. D. Allen, I. C. Ambridge, and T. T. Tidwell, J. Org. Chem., 48,
4527 (1983).